IFN-alpha is not sufficient to drive Th1 development due to lack of stable T-bet expression
- PMID: 17785816
- PMCID: PMC2927332
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3792
IFN-alpha is not sufficient to drive Th1 development due to lack of stable T-bet expression
Abstract
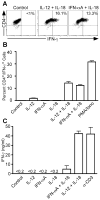
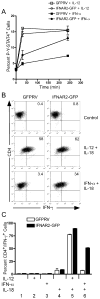
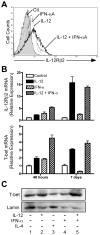
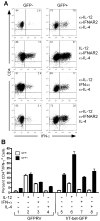
During inflammatory immune responses, the innate cytokine IL-12 promotes CD4+ Th-1 development through the activation of the second messenger STAT4 and the subsequent expression of T-bet. In addition, type I IFN (IFN-alphabeta), secreted primarily during viral and intracellular bacterial infections, can promote STAT4 activation in human CD4+ T cells. However, the role of IFN-alphabeta in regulating Th1 development is controversial, and previous studies have suggested a species-specific pathway leading to Th1 development in human but not mouse CD4+ T cells. In this study, we found that although both IFN-alpha and IL-12 can promote STAT4 activation, IFN-alpha failed to promote Th1 commitment in human CD4+ T cells. The difference between these innate signaling pathways lies with the ability of IL-12 to promote sustained STAT4 tyrosine phosphorylation, which correlated with stable T-bet expression in committed Th1 cells. IFN-alpha did not promote Th1 development in human CD4+ T cells because of attenuated STAT4 phosphorylation, which was insufficient to induce stable expression of T-bet. Further, the defect in IFN-alpha-driven Th1 development was corrected by ectopic expression of T-bet within primary naive human CD4+ T cells. These results indicate that IL-12 remains unique in its ability to drive Th1 development in human CD4+ T cells and that IFN-alpha lacks this activity due to its inability to promote sustained T-bet expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intestinal irradiation and fibrosis in a Th1-deficient environment.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Sep 1;84(1):266-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.11.027. Epub 2012 Feb 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22336200
-
IL-12, but not IFN-alpha, promotes STAT4 activation and Th1 development in murine CD4+ T cells expressing a chimeric murine/human Stat2 gene.J Immunol. 2005 Jan 1;174(1):294-301. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.1.294. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15611252
-
Regulation of IFN-gamma production by B effector 1 cells: essential roles for T-bet and the IFN-gamma receptor.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 1;174(11):6781-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.11.6781. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15905519
-
T helper differentiation proceeds through Stat1-dependent, Stat4-dependent and Stat4-independent phases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;238:13-26. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-09709-0_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10087648 Review.
-
The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:589672. doi: 10.1155/2014/589672. Epub 2014 May 13. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24901011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAT2: A shape-shifting anti-viral super STAT.JAKSTAT. 2013 Jan 1;2(1):e23633. doi: 10.4161/jkst.23633. JAKSTAT. 2013. PMID: 24058798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of effector and memory T-cell functions by type I interferon.Immunology. 2011 Apr;132(4):466-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03412.x. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 21320124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I IFN-dependent T cell activation is mediated by IFN-dependent dendritic cell OX40 ligand expression and is independent of T cell IFNR expression.J Immunol. 2012 Jan 15;188(2):585-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102550. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22156349 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-α suppresses GATA3 transcription from a distal exon and promotes H3K27 trimethylation of the CNS-1 enhancer in human Th2 cells.J Immunol. 2014 Jun 15;192(12):5687-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301908. Epub 2014 May 9. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24813204 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oncolytic Newcastle Disease Virus as Cutting Edge between Tumor and Host.Biology (Basel). 2013 Jul 2;2(3):936-75. doi: 10.3390/biology2030936. Biology (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24833054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Boonstra A, Asselin-Paturel C, Gilliet M, Crain C, Trinchieri G, Liu YJ, O’Garra A. Flexibility of mouse classical and plasmacytoid-derived dendritic cells in directing T helper type 1 and 2 cell development: dependency on antigen dose and differential toll-like receptor ligation. J Exp Med. 2003;197:101–109. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:133–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

