Optimizing efficacy of amphotericin B through nanomodification
- PMID: 17722276
- PMCID: PMC2676632
- DOI: 10.2147/nano.2006.1.4.417
Optimizing efficacy of amphotericin B through nanomodification
Abstract
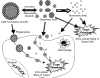
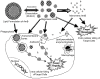
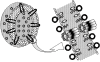
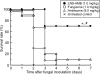
Fungal infections and leishmaniasis are an important cause of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised patients. The macrolide polyene antibiotic amphotericin B (AmB) has long been recognized as a powerful fungicidal and leishmanicidal drug. A conventional intravenous dosage form of AmB, AmB- deoxycholate (Fungizone or D-AmB), is the most effective clinically available for treating fungal and parasitic (leishmaniasis) infections. However, the clinical efficacy of AmB is limited by its adverse effects mainly nephrotoxicity. Efforts to lower the toxicity are based on synthesis of AmB analogues such as AmB esters or preparation of AmB-lipid associations in the forms of liposomal AmB (L-AmB or AmBisome), AmB lipid complex (Abelcet or ABLC), AmB colloidal dispersion (Amphocil or ABCD), and intralipid AmB. These newer formulations are substantially more expensive, but allow patients to receive higher doses for longer periods of time with decreased renal toxicity than conventional AmB. Modifications of liposomal surface in order to avoid RES uptake, thus increased targetability has been attempted. Emulsomes and other nanoparticles are special carrier systems for intracellular localization in macrophage rich organs like liver and spleen. Injectable nano-carriers have important potential applications as in site-specific drug delivery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drug delivery system of anti-fungal and parasitic agents.Curr Pharm Des. 2002;8(6):433-40. doi: 10.2174/1381612023395916. Curr Pharm Des. 2002. PMID: 12069380 Review.
-
Optimizing efficacy of Amphotericin B through nanomodification.Int J Nanomedicine. 2007;2(3):301-13. Int J Nanomedicine. 2007. PMID: 18019830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amphotericin B formulations: a comparative review of efficacy and toxicity.Drugs. 2013 Jun;73(9):919-34. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0069-4. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23729001 Review.
-
Amphotericin-B colloidal dispersion. A review of its use against systemic fungal infections and visceral leishmaniasis.Drugs. 1998 Sep;56(3):365-83. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199856030-00008. Drugs. 1998. PMID: 9777313 Review.
-
Liposomal and lipid-based formulations of amphotericin B.Leukemia. 1996 Jun;10 Suppl 2:s93-6. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8649062 Review.
Cited by
-
Local amphotericin B therapy for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A systematic review.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Apr 16;18(4):e0012127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012127. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38626196 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Novel Oral Amphotericin B Formulations for the Treatment of Parasitic Infections.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 28;14(11):2316. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112316. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Synthesis and Purification of Magnetoliposomes for Potential Applications in the Gastrointestinal Delivery of Difficult-to-Transport Drugs.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 28;14(2):315. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020315. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214047 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Antifungal Agents and Their Activity against Aspergillus Species.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Oct 9;6(4):213. doi: 10.3390/jof6040213. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicinal products: a survey on specific toxicity and side effects.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Aug 22;12:6107-6129. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S139687. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28883724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abra RM, Hunt CA. Liposome disposition in vivo. III. Dose and vesicle–size effects. Biocim Biophys Acta. 1981;666:493–503. - PubMed
-
- Adler-Moore JP, Chiang S, Satorius A, et al. Treatment of murine Candidosis and cryptococcosis with a unilamellar liposomal amphotericin B formulation (AmBisome) J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991;28(Suppl B):63–71. - PubMed
-
- Adler-Moore JP, Fujii G, Lee MJA, et al. In vitro and in vivo interactions of AmBisome with pathogenic fungi. J Liposome Res. 1993;3:151–6.
-
- Adler-Moore JP, Proffitt RT. AmBisome: long circulating formulation of Amphotericin B. In: Woodle MC, Storm G, editors. Long Circulating Liposomes: Old drugs, New Therapeutics. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1998. pp. 185–206.
-
- Adler-Moore J, Proffitt RT. AmBisome: liposomal formulation, structure, mechanism of action and preclinical experience. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;49(Suppl S1):21–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

