Alveolar epithelial beta2-adrenergic receptors
- PMID: 17709598
- PMCID: PMC2214676
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0198TR
Alveolar epithelial beta2-adrenergic receptors
Abstract
beta(2)-adrenergic receptors are present throughout the lung, including the alveolar airspace, where they play an important role for regulation of the active Na(+) transport needed for clearance of excess fluid out of alveolar airspace. beta(2)-adrenergic receptor signaling is required for up-regulation of alveolar epithelial active ion transport in the setting of excess alveolar edema. The positive, protective effects of beta(2)-adrenergic receptor signaling on alveolar active Na(+) transport in normal and injured lungs provide substantial support for the use of beta-adrenergic agonists to accelerate alveolar fluid clearance in patients with cardiogenic and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. In this review, we summarize the role of beta(2)-adrenergic receptors in the alveolar epithelium with emphasis on their role in the regulation of alveolar active Na(+) transport in normal and injured lungs.
Figures
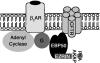
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of alveolar epithelial active Na+ transport is dependent on beta2-adrenergic receptor signaling.Circ Res. 2004 Apr 30;94(8):1091-100. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000125623.56442.20. Epub 2004 Mar 11. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15016730
-
Interdependency of beta-adrenergic receptors and CFTR in regulation of alveolar active Na+ transport.Circ Res. 2005 May 13;96(9):999-1005. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000164554.21993.AC. Epub 2005 Mar 31. Circ Res. 2005. PMID: 15802612
-
Clinically relevant concentrations of beta2-adrenergic agonists stimulate maximal cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent airspace fluid clearance and decrease pulmonary edema in experimental acid-induced lung injury.Crit Care Med. 2004 Jul;32(7):1470-6. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000129489.34416.0e. Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 15241090
-
Effects of beta2-adrenergic receptor overexpression on alveolar epithelial active transport.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002 Dec;110(6 Suppl):S242-6. doi: 10.1067/mai.2002.129706. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12464931 Review.
-
Lung edema clearance: 20 years of progress: invited review: alveolar edema fluid clearance in the injured lung.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002 Dec;93(6):2207-13. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01201.2001. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002. PMID: 12433940 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of α - and β -Adrenergic Mechanisms to the Development of Pulmonary Edema.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:829504. doi: 10.6064/2012/829504. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 24278744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of β2 adrenergic receptor agonists in experimental acute lung injury.FASEB J. 2012 May;26(5):2137-44. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-201640. Epub 2012 Feb 7. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22318967 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of the kidney, vessels, and heart with administration of β2 adrenergic receptor agonists in patients susceptible to acute respiratory distress syndrome.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Jun 1;189(11):1445-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201404-0610LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24881947 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The effects of salbutamol on epithelial ion channels depend on the etiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome but not the route of administration.Respir Res. 2014 May 2;15(1):56. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-15-56. Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 24886221 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome; A Review of Recent Updates and a Glance into the Future.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 24;13(9):1528. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13091528. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mutlu GM, Koch WJ, Factor P. Alveolar epithelial beta 2-adrenergic receptors: their role in regulation of alveolar active sodium transport. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;170:1270–1275. - PubMed
-
- Granneman JG. The putative beta4-adrenergic receptor is a novel state of the beta1-adrenergic receptor. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001;280:E199–E202. - PubMed
-
- Spina D, Rigby PJ, Paterson JW, Goldie RG. Autoradiographic localization of beta-adrenoceptors in asthmatic human lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989;140:1410–1415. - PubMed
-
- Carstairs JR, Nimmo AJ, Barnes PJ. Autoradiographic visualization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in human lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 1985;132:541–547. - PubMed
-
- Liebler JM, Borok Z, Li X, Zhou B, Sandoval AJ, Kim KJ, Crandall ED. Alveolar epithelial type I cells express beta2-adrenergic receptors and G-protein receptor kinase 2. J Histochem Cytochem 2004;52:759–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

