p180 is involved in the interaction between the endoplasmic reticulum and microtubules through a novel microtubule-binding and bundling domain
- PMID: 17634287
- PMCID: PMC1995732
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-12-1125
p180 is involved in the interaction between the endoplasmic reticulum and microtubules through a novel microtubule-binding and bundling domain
Abstract
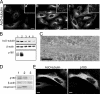
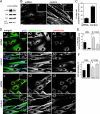
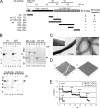
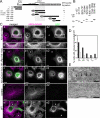
p180 was originally reported as a ribosome-binding protein on the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane, although its precise role in animal cells has not yet been elucidated. Here, we characterized a new function of human p180 as a microtubule-binding and -modulating protein. Overexpression of p180 in mammalian cells induced an elongated morphology and enhanced acetylated microtubules. Consistently, electron microscopic analysis clearly revealed microtubule bundles in p180-overexpressing cells. Targeted depletion of endogenous p180 by small interfering RNAs led to aberrant patterns of microtubules and endoplasmic reticulum in mammalian cells, suggesting a specific interaction between p180 and microtubules. In vitro sedimentation assays using recombinant polypeptides revealed that p180 bound to microtubules directly and possessed a novel microtubule-binding domain (designated MTB-1). MTB-1 consists of a predicted coiled-coil region and repeat domain, and strongly promoted bundle formation both in vitro and in vivo when expressed alone. Overexpression of p180 induced acetylated microtubules in cultured cells in an MTB-1-dependent manner. Thus, our data suggest that p180 mediates interactions between the endoplasmic reticulum and microtubules mainly through the novel microtubule-binding and -bundling domain MTB-1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expansion of the trans-Golgi network following activated collagen secretion is supported by a coiled-coil microtubule-bundling protein, p180, on the ER.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Feb 1;316(3):329-40. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 19932094
-
Regulation of polysome assembly on the endoplasmic reticulum by a coiled-coil protein, p180.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(7):3006-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1197. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22156060 Free PMC article.
-
An endoplasmic reticulum protein, p180, is highly expressed in human cytomegalovirus-permissive cells and interacts with the tegument protein encoded by UL48.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(5):2350-62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2350-2362.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11836413 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of procollagen biosynthesis by p180 through augmented ribosome association on the endoplasmic reticulum in response to stimulated secretion.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 24;285(39):29941-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.094607. Epub 2010 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20647306 Free PMC article.
-
A novel direct interaction of endoplasmic reticulum with microtubules.EMBO J. 1998 Nov 2;17(21):6168-77. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.21.6168. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9799226 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of ribosome binding protein 1 (RRBP1) in breast cancer.Clin Proteomics. 2012 Jun 18;9(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1559-0275-9-7. Clin Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22709790 Free PMC article.
-
La Autoantigen Induces Ribosome Binding Protein 1 (RRBP1) Expression through Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES)-Mediated Translation during Cellular Stress Condition.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 20;17(7):1174. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071174. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27447629 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive sheet-to-tubule transformation is a general mechanism for endoplasmic reticulum partitioning in dividing mammalian cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jul;23(13):2424-32. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-12-0950. Epub 2012 May 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22573885 Free PMC article.
-
The role of altered protein acetylation in neurodegenerative disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;14:1025473. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1025473. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36688174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valosin-containing protein-interacting membrane protein (VIMP) links the endoplasmic reticulum with microtubules in concert with cytoskeleton-linking membrane protein (CLIMP)-63.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 29;289(35):24304-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.571372. Epub 2014 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25008318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan V. J., Schroer T. A. Membrane motors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999;11:476–482. - PubMed
-
- Baumann O., Walz B. Endoplasmic reticulum of animal cells and its organization into structural and functional domains. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2001;205:149–214. - PubMed
-
- Bulinski J. C., Gundersen G. G. Stabilization of post-translational modification of microtubules during cellular morphogenesis. Bioessays. 1991;13:285–293. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

