Eps15 and Dap160 control synaptic vesicle membrane retrieval and synapse development
- PMID: 17620409
- PMCID: PMC2064449
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200701030
Eps15 and Dap160 control synaptic vesicle membrane retrieval and synapse development
Abstract
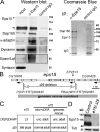
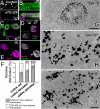
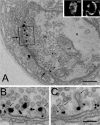
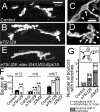
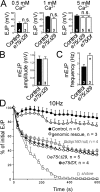
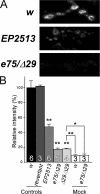
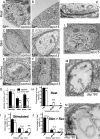
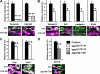
Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway substrate clone 15 (Eps15) is a protein implicated in endocytosis, endosomal protein sorting, and cytoskeletal organization. Its role is, however, still unclear, because of reasons including limitations of dominant-negative experiments and apparent redundancy with other endocytic proteins. We generated Drosophila eps15-null mutants and show that Eps15 is required for proper synaptic bouton development and normal levels of synaptic vesicle (SV) endocytosis. Consistent with a role in SV endocytosis, Eps15 moves from the center of synaptic boutons to the periphery in response to synaptic activity. The endocytic protein, Dap160/intersectin, is a major binding partner of Eps15, and eps15 mutants phenotypically resemble dap160 mutants. Analyses of eps15 dap160 double mutants suggest that Eps15 functions in concert with Dap160 during SV endocytosis. Based on these data, we hypothesize that Eps15 and Dap160 promote the efficiency of endocytosis from the plasma membrane by maintaining high concentrations of multiple endocytic proteins, including dynamin, at synapses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dap160/intersectin acts as a stabilizing scaffold required for synaptic development and vesicle endocytosis.Neuron. 2004 Jul 22;43(2):193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.029. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15260956
-
Dap160/intersectin scaffolds the periactive zone to achieve high-fidelity endocytosis and normal synaptic growth.Neuron. 2004 Jul 22;43(2):207-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.001. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15260957
-
An Endocytic Scaffolding Protein together with Synapsin Regulates Synaptic Vesicle Clustering in the Drosophila Neuromuscular Junction.J Neurosci. 2015 Nov 4;35(44):14756-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1675-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26538647 Free PMC article.
-
Synapse scaffolding: intersection of endocytosis and growth.Curr Biol. 2004 Oct 5;14(19):R853-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.042. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15458667 Review.
-
Stonins--specialized adaptors for synaptic vesicle recycling and beyond?Traffic. 2010 Jan;11(1):8-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00971.x. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 19732400 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Eps15 as antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibodies aa2 and ab52 of the Wuerzburg Hybridoma Library against Drosophila brain.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029352. Epub 2011 Dec 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22206011 Free PMC article.
-
Sialyltransferase regulates nervous system function in Drosophila.J Neurosci. 2010 May 5;30(18):6466-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5253-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20445073 Free PMC article.
-
ITSN-1 controls vesicle recycling at the neuromuscular junction and functions in parallel with DAB-1.Traffic. 2008 May;9(5):742-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00712.x. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18298590 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic vesicle endocytosis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Sep 1;4(9):a005645. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005645. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22763746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila cyfip regulates synaptic development and endocytosis by suppressing filamentous actin assembly.PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003450. Epub 2013 Apr 4. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23593037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bache, K.G., C. Raiborg, A. Mehlum, and H. Stenmark. 2003. STAM and Hrs are subunits of a multivalent ubiquitin-binding complex on early endosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 278:12513–12521. - PubMed
-
- Bean, A.J., S. Davanger, M.F. Chou, B. Gerhardt, S. Tsujimoto, and Y. Chang. 2000. Hrs-2 regulates receptor-mediated endocytosis via interactions with Eps15. J. Biol. Chem. 275:15271–15278. - PubMed
-
- Bellen, H.J., and V. Budnik. 2000. The neuromuscular junction. In Drosophila Protocols. W. Sullivan, M. Ashburner, and R.S. Hawley, editors. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. 175–199.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

