Inhibition of c-Myc activity by ribosomal protein L11
- PMID: 17599065
- PMCID: PMC1933407
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601776
Inhibition of c-Myc activity by ribosomal protein L11
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2009 Apr 8;28(7):993
Abstract
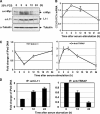
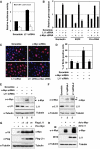
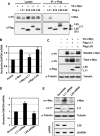
The c-Myc oncoprotein promotes cell growth by enhancing ribosomal biogenesis through upregulation of RNA polymerases I-, II-, and III-dependent transcription. Overexpression of c-Myc and aberrant ribosomal biogenesis leads to deregulated cell growth and tumorigenesis. Hence, c-Myc activity and ribosomal biogenesis must be regulated in cells. Here, we show that ribosomal protein L11, a component of the large subunit of the ribosome, controls c-Myc function through a negative feedback mechanism. L11 is transcriptionally induced by c-Myc, and overexpression of L11 inhibits c-Myc-induced transcription and cell proliferation. Conversely, reduction of endogenous L11 by siRNA increases these c-Myc activities. Mechanistically, L11 binds to the Myc box II (MB II), inhibits the recruitment of the coactivator TRRAP, and reduces histone H4 acetylation at c-Myc target gene promoters. In response to serum stimulation or serum starvation, L11 and TRRAP display inverse promoter-binding profiles. In addition, L11 regulates c-Myc levels. These results identify L11 as a feedback inhibitor of c-Myc and suggest a novel role for L11 in regulating c-Myc-enhanced ribosomal biogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-130a associates with ribosomal protein L11 to suppress c-Myc expression in response to UV irradiation.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 20;6(2):1101-14. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2728. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25544755 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein L11 associates with c-Myc at 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes and regulates their expression.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12587-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056259. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20194507 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback regulation of c-Myc by ribosomal protein L11.Cell Cycle. 2007 Nov 15;6(22):2735-41. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.22.4895. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 18032916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal protein S14 negatively regulates c-Myc activity.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21793-801. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445122. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23775087 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between c-Myc and ribosome in ribosomal biogenesis and cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Oct 15;105(3):670-7. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21895. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18773413 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-130a associates with ribosomal protein L11 to suppress c-Myc expression in response to UV irradiation.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 20;6(2):1101-14. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2728. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25544755 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding motif protein 10 inactivates c-Myc by partnering with ribosomal proteins uL18 and uL5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 5;120(49):e2308292120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308292120. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38032932 Free PMC article.
-
circ-hnRNPU inhibits NONO-mediated c-Myc transactivation and mRNA stabilization essential for glycosylation and cancer progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 23;42(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02898-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37993881 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of the Physical Interaction between Rpl22 and the Transposable Element Doc5, a Heterochromatic Transposon of Drosophila melanogaster.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 16;12(12):1997. doi: 10.3390/genes12121997. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946947 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of the tumor microenvironment during breast cancer progression.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(1):R7. doi: 10.1186/bcr2222. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19187537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL (1985) The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature 318: 533–538 - PubMed
-
- Adhikary S, Eilers M (2005) Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 635–645 - PubMed
-
- Adhikary S, Marinoni F, Hock A, Hulleman E, Popov N, Beier R, Bernard S, Quarto M, Capra M, Goettig S, Kogel U, Scheffner M, Helin K, Eilers M (2005) The ubiquitin ligase HectH9 regulates transcriptional activation by Myc and is essential for tumor cell proliferation. Cell 123: 409–421 - PubMed
-
- Amati B, Dalton S, Brooks MW, Littlewood TD, Evan GI, Land H (1992) Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature 359: 423–426 - PubMed
-
- Arabi A, Wu S, Ridderstrale K, Bierhoff H, Shiue C, Fatyol K, Fahlen S, Hydbring P, Soderberg O, Grummt I, Larsson LG, Wright AP (2005) c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat Cell Biol 7: 303–310 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

