Zfra affects TNF-mediated cell death by interacting with death domain protein TRADD and negatively regulates the activation of NF-kappaB, JNK1, p53 and WOX1 during stress response
- PMID: 17567906
- PMCID: PMC1904229
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-50
Zfra affects TNF-mediated cell death by interacting with death domain protein TRADD and negatively regulates the activation of NF-kappaB, JNK1, p53 and WOX1 during stress response
Abstract
Background: Zfra is a 31-amino-acid zinc finger-like protein, which is known to regulate cell death by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and overexpressed TNF receptor- or Fas-associated death domain proteins (TRADD and FADD). In addition, Zfra undergoes self-association and interacts with c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in response to stress stimuli. To further delineate the functional properties of Zfra, here we investigated Zfra regulation of the activation of p53, WOX1 (WWOX or FOR), NF-kappaB, and JNK1 under apoptotic stress.
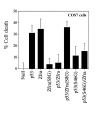
Results: Transiently overexpressed Zfra caused growth suppression and apoptotic death of many but not all types of cells. Zfra either enhanced or blocked cell death caused by TRADD, FADD, or receptor-interacting protein (RIP) in a dose-related manner. This modulation is related with Zfra binding with TRADD, NF-kappaB, JNK1 and WOX1, as determined by GST pull-down analysis, co-immunoprecipitation, and mapping by yeast two-hybrid analysis. Functionally, transiently overexpressed Zfra sequestered NF-kappaB (p65), WOX1, p53 and phospho-ERK (extracellular signal-activated kinase) in the cytoplasm, and TNF or UV light could not effectively induce nuclear translocation of these proteins. Zfra counteracted the apoptotic functions of Tyr33-phosphorylated WOX1 and Ser46-phosphorylated p53. Alteration of Ser8 to Gly abolished the apoptotic function of Zfra and its regulation of WOX1 and p53.
Conclusion: In response to TNF, Zfra is upregulated and modulates TNF-mediated cell death via interacting with TRADD, FADD and RIP (death-inducing signaling complex) at the receptor level, and downstream effectors NF-kappaB, p53, WOX1, and JNK1.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of a small-size peptide Zfra that regulates the cytotoxic function of tumor necrosis factor by interacting with JNK1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Feb 11;327(2):415-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.025. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 15629131
-
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate protects against tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced necrotic cell death by modulating the recruitment of TNF receptor 1-associated death domain and receptor-interacting protein into the TNF receptor 1 signaling complex: Implication for the regulatory role of protein kinase C.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;70(3):1099-108. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.025452. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16798936
-
Evidence that TNF-TNFR1-TRADD-TRAF2-RIP-TAK1-IKK pathway mediates constitutive NF-kappaB activation and proliferation in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2007 Mar 1;26(10):1385-97. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209945. Epub 2006 Sep 4. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16953224
-
Pursuing different 'TRADDes': TRADD signaling induced by TNF-receptor 1 and the Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1.Biol Chem. 2008 Oct;389(10):1261-71. doi: 10.1515/BC.2008.144. Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18713013 Review.
-
Exploring cell death mechanisms by analyzing signaling cascades of the TNF/NGF receptor family.Behring Inst Mitt. 1996 Oct;(97):144-55. Behring Inst Mitt. 1996. PMID: 8950472 Review.
Cited by
-
Zfra induction of memory anticancer response via a novel immune cell.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Jul 28;5(9):e1213935. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1213935. eCollection 2016. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 27757310 Free PMC article.
-
HYAL-2-WWOX-SMAD4 Signaling in Cell Death and Anticancer Response.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Dec 6;4:141. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00141. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27999774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zfra Overrides WWOX in Suppressing the Progression of Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3507. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063507. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of WWOX and NF-κB in lung cancer progression.Transl Respir Med. 2013 Dec;1(1):15. doi: 10.1186/2213-0802-1-15. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Transl Respir Med. 2013. PMID: 27234396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UV irradiation/cold shock-mediated apoptosis is switched to bubbling cell death at low temperatures.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 10;6(10):8007-18. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3153. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25779665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bednarek AK, Laflin KJ, Daniel RL, Liao Q, Hawkins KA, Aldaz CM. WWOX, a novel WW domain-containing protein mapping to human chromosome 16q23.3-24.1, a region frequently affected in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2140–2145. - PubMed
-
- Ried K, Finnis M, Hobson L, Mangelsdorf M, Dayan S, Nancarrow JK, Woollatt E, Kremmidiotis G, Gardner A, Venter D, Baker E, Richards RI. Common chromosomal fragile site FRAD16D sequence: identification of the FOR gene spanning FRAD16D and homozygous deletions and translcoation breakpoints in cancer cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1651–1663. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.11.1651. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

