Cdc14-regulated midzone assembly controls anaphase B
- PMID: 17562791
- PMCID: PMC2064359
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200702145
Cdc14-regulated midzone assembly controls anaphase B
Abstract
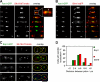
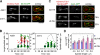
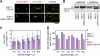
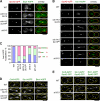
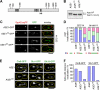
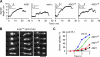
Spindle elongation in anaphase of mitosis is a cell cycle-regulated process that requires coordination between polymerization, cross-linking, and sliding of microtubules (MTs). Proteins that assemble at the spindle midzone may be important for this process. In this study, we show that Ase1 and the separase-Slk19 complex drive midzone assembly in yeast. Whereas the conserved MT-bundling protein Ase1 establishes a midzone, separase-Slk19 is required to focus and center midzone components. An important step leading to spindle midzone assembly is the dephosphorylation of Ase1 by the protein phosphatase Cdc14 at the beginning of anaphase. Failure to dephosphorylate Ase1 delocalizes midzone proteins and delays the second, slower phase of anaphase B. In contrast, in cells expressing nonphosphorylated Ase1, anaphase spindle extension is faster, and spindles frequently break. Cdc14 also controls the separase-Slk19 complex indirectly via the Aurora B kinase. Thus, Cdc14 regulates spindle midzone assembly and function directly through Ase1 and indirectly via the separase-Slk19 complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Separase regulates INCENP-Aurora B anaphase spindle function through Cdc14.Science. 2003 Dec 19;302(5653):2120-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1091936. Epub 2003 Nov 6. Science. 2003. PMID: 14605209
-
Assembling the spindle midzone in the right place at the right time.Cell Cycle. 2008 Feb 1;7(3):283-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.3.5349. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18235228 Review.
-
Phospho-regulation of the Cdc14/Clp1 phosphatase delays late mitotic events in S. pombe.Dev Cell. 2006 Sep;11(3):423-30. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.07.016. Dev Cell. 2006. PMID: 16950131
-
Phosphorylation-dependent protein interactions at the spindle midzone mediate cell cycle regulation of spindle elongation.Dev Cell. 2009 Aug;17(2):244-56. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.011. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19686685
-
Mechanisms of the Ase1/PRC1/MAP65 family in central spindle assembly.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019 Dec;94(6):2033-2048. doi: 10.1111/brv.12547. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019. PMID: 31343816 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell cycle regulators interact with pathways that modulate microtubule stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Dec;10(12):1705-13. doi: 10.1128/EC.05215-11. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 22037179 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of Pac1/LIS1-mediated dynein targeting: Implications for regulation of dynein activity in budding yeast.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011 Mar;68(3):157-74. doi: 10.1002/cm.20502. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21294277 Free PMC article.
-
Ipl1/Aurora-dependent phosphorylation of Sli15/INCENP regulates CPC-spindle interaction to ensure proper microtubule dynamics.J Cell Biol. 2011 Jul 11;194(1):137-53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201009137. Epub 2011 Jul 4. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21727193 Free PMC article.
-
Spindle assembly requires complete disassembly of spindle remnants from the previous cell cycle.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(2):258-67. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0701. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22090343 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-regulated interaction between kinesin-6 Klp9p and microtubule bundler Ase1p promotes spindle elongation.Dev Cell. 2009 Aug;17(2):257-67. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.012. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19686686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araki, H., K. Awane, N. Ogawa, and Y. Oshima. 1992. The CDC26 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for cell growth only at high temperature. Mol. Gen. Genet. 231:329–331. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian, M.K., E. Bi, and M. Glotzer. 2004. Comparative analysis of cytokinesis in budding yeast, fission yeast and animal cells. Curr. Biol. 14:R806–R818. - PubMed
-
- Belmont, L.D., A.A. Hyman, K.E. Sawin, and T.J. Mitchison. 1990. Real-time visualization of cell cycle-dependent changes in microtubule dynamics in cytoplasmic extracts. Cell. 62:579–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

