Cannabinoids mediate analgesia largely via peripheral type 1 cannabinoid receptors in nociceptors
- PMID: 17558404
- PMCID: PMC2234438
- DOI: 10.1038/nn1916
Cannabinoids mediate analgesia largely via peripheral type 1 cannabinoid receptors in nociceptors
Abstract
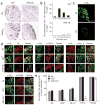
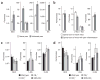
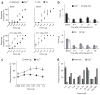
Although endocannabinoids constitute one of the first lines of defense against pain, the anatomical locus and the precise receptor mechanisms underlying cannabinergic modulation of pain are uncertain. Clinical exploitation of the system is severely hindered by the cognitive deficits, memory impairment, motor disturbances and psychotropic effects resulting from the central actions of cannabinoids. We deleted the type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1) specifically in nociceptive neurons localized in the peripheral nervous system of mice, preserving its expression in the CNS, and analyzed these genetically modified mice in preclinical models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. The nociceptor-specific loss of CB1 substantially reduced the analgesia produced by local and systemic, but not intrathecal, delivery of cannabinoids. We conclude that the contribution of CB1-type receptors expressed on the peripheral terminals of nociceptors to cannabinoid-induced analgesia is paramount, which should enable the development of peripherally acting CB1 analgesic agonists without any central side effects.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid analgesia.Pharmacol Ther. 2002 Aug;95(2):127-35. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00252-8. Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12182960 Review.
-
Mode of action of cannabinoids on nociceptive nerve endings.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Jun;196(1):79-88. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1762-0. Epub 2009 Mar 22. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19306092 Review.
-
[The cannabinoid system and pain: towards new drugs?].J Soc Biol. 2009;203(1):99-106. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2009002. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Soc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19358815 Review. French.
-
Cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor--pharmacology, role in pain and recent developments in emerging CB1 agonists.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 Aug;10(5):536-44. doi: 10.2174/187152711796235005. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21631407 Review.
-
Acetaminophen Relieves Inflammatory Pain through CB1 Cannabinoid Receptors in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 10;38(2):322-334. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1945-17.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 22. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29167401 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Changes of blood endocannabinoids during anaesthesia: a special case for fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition by propofol?Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Jul;74(1):54-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04175.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22242687 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2 in neuropathic pain.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jul;123(7):3002-13. doi: 10.1172/JCI68996. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23778145 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid receptors: nomenclature and pharmacological principles.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Jul 2;38(1):4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22421596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitors produce anti-allodynic effects in mice through distinct cannabinoid receptor mechanisms.J Pain. 2010 Dec;11(12):1420-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Pain. 2010. PMID: 20554481 Free PMC article.
-
Endocannabinoid signalling: has it got rhythm?Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;160(3):530-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00790.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Walker JM, Hohmann AG. Cannabinoid mechanisms of pain suppression. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2005;168:509–554. - PubMed
-
- Freund TF, Katona I, Piomelli D. Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1017–1066. - PubMed
-
- Piomelli D. The endocannabinoid system: a drug discovery perspective. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;6:672–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS039518-01A2/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS 038253/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000286-04/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA11322/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011322-02/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000286/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038253-01S1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011322/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AA000375-02/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- DA00286/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038253/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

