Inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cause defects in the postendocytic sorting of beta2-adrenergic receptors
- PMID: 17553490
- PMCID: PMC2034330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.04.034
Inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cause defects in the postendocytic sorting of beta2-adrenergic receptors
Abstract
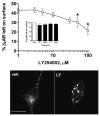
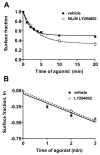
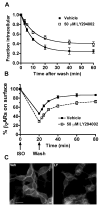
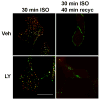
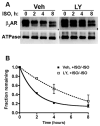
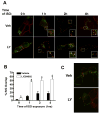
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors have been shown to affect endocytosis or subsequent intracellular sorting in various receptor systems. Agonist-activated beta(2)-adrenergic receptors undergo desensitization by mechanisms that include the phosphorylation, endocytosis and degradation of receptors. Following endocytosis, most internalized receptors are sorted to the cell surface, but some proportion is sorted to lysosomes for degradation. It is not known what governs the ratio of receptors that recycle versus receptors that undergo degradation. To determine if phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases regulate beta(2)-adrenergic receptor trafficking, HEK293 cells stably expressing these receptors were treated with the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors LY294002 or wortmannin. We then studied agonist-induced receptor endocytosis and postendocytic sorting, including recycling and degradation of the internalized receptors. Both inhibitors amplified the internalization of receptors after exposure to the beta-agonist isoproterenol, which was attributable to the sorting of a significant fraction of receptors to an intracellular compartment from which receptor recycling did not occur. The initial rate of beta(2)-adrenergic receptor endocytosis and the default rate of receptor recycling were not significantly altered. During prolonged exposure to agonist, LY294002 slowed the degradation rate of beta(2)-adrenergic receptors and caused the accumulation of receptors within rab7-positive vesicles. These results suggest that phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors (1) cause a misrouting of beta(2)-adrenergic receptors into vesicles that are neither able to efficiently recycle to the surface nor sort to lysosomes, and (2) delays the movement of receptors from late endosomes to lysosomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rab11 regulates the recycling and lysosome targeting of beta2-adrenergic receptors.J Cell Sci. 2004 Jul 1;117(Pt 15):3107-17. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01168. Epub 2004 Jun 9. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15190120
-
A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the beta2-adrenergic receptor.Nature. 1999 Sep 16;401(6750):286-90. doi: 10.1038/45816. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10499588
-
Differential PI 3-kinase dependence of early and late phases of recycling of the internalized AT1 angiotensin receptor.J Cell Biol. 2002 Jun 24;157(7):1211-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200111013. Epub 2002 Jun 17. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12070129 Free PMC article.
-
Postendocytic Sorting of Adrenergic and Opioid Receptors: New Mechanisms and Functions.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;132:189-206. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26055059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptor-associated sorting protein 1 regulates the postendocytic sorting of seven-transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacology. 2010;86(1):22-9. doi: 10.1159/000314161. Epub 2010 Jun 26. Pharmacology. 2010. PMID: 20693822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
G-protein coupled receptor resensitization-appreciating the balancing act of receptor function.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012 May 30. Online ahead of print. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22697395 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Is Essential for Canonical GPCR Signaling.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;91(1):65-73. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.106252. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27821547 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of acute and chronic nadolol treatment on β2AR signaling in HEK293 cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;383(2):209-16. doi: 10.1007/s00210-010-0591-9. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21225244
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Rab5 GTPase inversely regulate the Smad anchor for receptor activation (SARA) protein independently of transforming growth factor-β1.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):35815-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.380493. Epub 2012 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22942286 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptor protein-3 complex is required for Vangl2 trafficking and planar cell polarity of the inner ear.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Aug 15;30(18):2422-2434. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-08-0592. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31268833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tran TM, Friedman J, Qunaibi E, Baameur F, Moore RH, Clark RB. Characterization of agonist stimulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and G protein-coupled receptor kinase phosphorylation of the ®2-adrenergic receptor using phosphoserine-specific antibodies. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;65:196–206. - PubMed
-
- Yuan N, Friedman J, Whaley BS, Clark RB. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C consensus site mutations of the ®-adrenergic receptor. Effect on desensitization and stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:23032–23038. - PubMed
-
- Lohse MJ, Benovic JL, Codina J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. ®-arrestin: a protein that regulates ®-adrenergic function. Science. 1990;248:1547–1550. - PubMed
-
- Goodman OB, Jr, Krupnick JG, Santini F, Gurevich VV, Penn RB, Gagnon AW, Keen JH, Benovic JL. ®-arrestin acts as a clathrin adaptor in endocytosis of the ®2-adrenergic receptor. Nature. 1996;383:447–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

