Alveolar fluid clearance in acute lung injury: what have we learned from animal models and clinical studies?
- PMID: 17525842
- PMCID: PMC7095514
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-007-0662-7
Alveolar fluid clearance in acute lung injury: what have we learned from animal models and clinical studies?
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome continue to be significant causes of morbidity and mortality in the intensive care setting. The failure of patients to resolve the alveolar edema associated with these conditions is a major contributing factor to mortality; hence there is continued interest to understand the mechanisms of alveolar edema fluid clearance.
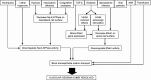
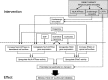
Discussion: The accompanying review by Vadász et al. details our current understanding of the signaling mechanisms and cellular processes that facilitate clearance of edema fluid from the alveolar compartment, and how these signaling processes may be exploited in the development of novel therapeutic strategies. To complement that report this review focuses on how intact organ and animal models and clinical studies have facilitated our understanding of alveolar edema fluid clearance in acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Furthermore, it considers how what we have learned from these animal and organ models and clinical studies has suggested novel therapeutic avenues to pursue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alveolar epithelium and Na,K-ATPase in acute lung injury.Intensive Care Med. 2007 Jul;33(7):1243-1251. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0661-8. Epub 2007 May 25. Intensive Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17530222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alveolar epithelial fluid clearance mechanisms are intact after moderate hyperoxic lung injury in rats.Chest. 1997 May;111(5):1381-8. doi: 10.1378/chest.111.5.1381. Chest. 1997. PMID: 9149598
-
Alveolar epithelial fluid transport in acute lung injury: new insights.Eur Respir J. 2002 Nov;20(5):1299-313. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.00401602. Eur Respir J. 2002. PMID: 12449188 Review.
-
Introduction to alveolar liquid clearance during lung injury: a crucial function--long ignored.Intensive Care Med. 2007 Jul;33(7):1241-1242. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0625-z. Intensive Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17530223 No abstract available.
-
Clinically relevant concentrations of beta2-adrenergic agonists stimulate maximal cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent airspace fluid clearance and decrease pulmonary edema in experimental acid-induced lung injury.Crit Care Med. 2004 Jul;32(7):1470-6. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000129489.34416.0e. Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 15241090
Cited by
-
Effect of ventilation pressure on alveolar fluid clearance and beta-agonist responses in mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Oct;297(4):L785-93. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00096.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19684202 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity Attenuates Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury by Modulating the STAT3-SOCS3 Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 20;12:720844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.720844. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34489970 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates CO2-induced alveolar epithelial dysfunction in rats and human cells by promoting Na,K-ATPase endocytosis.J Clin Invest. 2008 Feb;118(2):752-62. doi: 10.1172/JCI29723. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18188452 Free PMC article.
-
17β-estradiol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through PI3K/Akt/SGK1 mediated up-regulation of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in vivo and in vitro.Respir Res. 2014 Dec 31;15(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0159-1. Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 25551628 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Quzhou Fructus Aurantii Extract in Preventing and Treating Acute Lung Injury and Inflammation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):1698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20083-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374248 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

