Characterization of three classes of membrane proteins involved in fungal azole resistance by functional hyperexpression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17513564
- PMCID: PMC1951111
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00091-07
Characterization of three classes of membrane proteins involved in fungal azole resistance by functional hyperexpression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
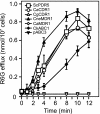
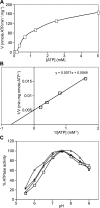
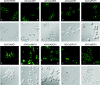
The study of eukaryotic membrane proteins has been hampered by a paucity of systems that achieve consistent high-level functional protein expression. We report the use of a modified membrane protein hyperexpression system to characterize three classes of fungal membrane proteins (ABC transporters Pdr5p, CaCdr1p, CaCdr2p, CgCdr1p, CgPdh1p, CkAbc1p, and CneMdr1p, the major facilitator superfamily transporter CaMdr1p, and the cytochrome P450 enzyme CaErg11p) that contribute to the drug resistance phenotypes of five pathogenic fungi and to express human P glycoprotein (HsAbcb1p). The hyperexpression system consists of a set of plasmids that direct the stable integration of a single copy of the expression cassette at the chromosomal PDR5 locus of a modified host Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, ADDelta. Overexpression of heterologous proteins at levels of up to 29% of plasma membrane protein was achieved. Membrane proteins were expressed with or without green fluorescent protein (GFP), monomeric red fluorescent protein, His, FLAG/His, Cys, or His/Cys tags. Most GFP-tagged proteins tested were correctly trafficked within the cell, and His-tagged proteins could be affinity purified. Kinetic analysis of ABC transporters indicated that the apparent K(m) value and the V(max) value of ATPase activities were not significantly affected by the addition of His tags. The efflux properties of seven fungal drug pumps were characterized by their substrate specificities and their unique patterns of inhibition by eight xenobiotics that chemosensitized S. cerevisiae strains overexpressing ABC drug pumps to fluconazole. The modified hyperexpression system has wide application for the study of eukaryotic membrane proteins and could also be used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug screening.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Analyses of Cladophialophora bantiana, a Major Cause of Cerebral Phaeohyphomycosis Provides Insight into Its Lifestyle, Virulence and Adaption in Host.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 29;11(8):e0161008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161008. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27570972 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic landscape of the DHA1 family in Candida auris and mapping substrate repertoire of CauMdr1.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Nov;106(21):7085-7097. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12189-2. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36184687
-
Exploring Cryptococcus neoformans CYP51 and Its Cognate Reductase as a Drug Target.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;8(12):1256. doi: 10.3390/jof8121256. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36547589 Free PMC article.
-
Fluconazole transport into Candida albicans secretory vesicles by the membrane proteins Cdr1p, Cdr2p, and Mdr1p.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Jun;9(6):960-70. doi: 10.1128/EC.00355-09. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20348384 Free PMC article.
-
ABC transporter Cdr1p contributes more than Cdr2p does to fluconazole efflux in fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans clinical isolates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Nov;52(11):3851-62. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00463-08. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18710914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott, A. 2000. Structures by numbers. Nature 408:130-132. - PubMed
-
- Balzi, E., W. Chen, S. Ulaszewski, E. Capieaux, and A. Goffeau. 1987. The multidrug resistance gene PDR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 262:16871-16879. - PubMed
-
- Bill, R. M. 2001. Yeast—a panacea for the structure-function analysis of membrane proteins? Curr. Genet. 40:157-171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

