High-avidity monoclonal antibodies against the human scavenger class B type I receptor efficiently block hepatitis C virus infection in the presence of high-density lipoprotein
- PMID: 17507483
- PMCID: PMC1951280
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00193-07
High-avidity monoclonal antibodies against the human scavenger class B type I receptor efficiently block hepatitis C virus infection in the presence of high-density lipoprotein
Abstract
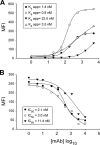
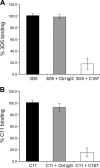
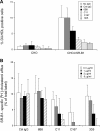
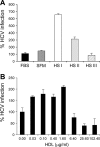
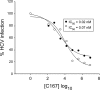
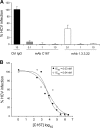
The human scavenger class B type 1 receptor (SR-B1/Cla1) was identified as a putative receptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) because it binds to soluble recombinant HCV envelope glycoprotein E2 (sE2). High-density lipoprotein (HDL), a natural SR-B1 ligand, was shown to increase the in vitro infectivity of retroviral pseudoparticles bearing HCV envelope glycoproteins and of cell culture-derived HCV (HCVcc), suggesting that SR-B1 promotes viral entry in an HDL-dependent manner. To determine whether SR-B1 participates directly in HCV infection or facilitates HCV entry through lipoprotein uptake, we generated a panel of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against native human SR-B1. Two of them, 3D5 and C167, bound to conformation-dependent SR-B1 determinants and inhibited the interaction of sE2 with SR-B1. These antibodies efficiently blocked HCVcc infection of Huh-7.5 hepatoma cells in a dose-dependent manner. To examine the role of HDL in SR-B1-mediated HCVcc infection, we set up conditions for HCVcc production and infection in serum-free medium. HCVcc efficiently infected Huh-7.5 cells in the absence of serum lipoproteins, and addition of HDL led to a twofold increase in infectivity. However, the HDL-induced enhancement of infection had no impact on the neutralization potency of MAb C167, despite its ability to inhibit both HDL binding to cells and SR-B1-mediated lipid transfer. Of note, MAb C167 also potently blocked Huh-7.5 infection by an HCV strain recovered from HCVcc-infected chimpanzees. These results demonstrate that SR-B1 is essential for infection with HCV produced in vitro and in vivo and suggest the possible use of anti-SR-B1 antibodies as therapeutic agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of scavenger receptor class B type I in hepatitis C virus entry: kinetics and molecular determinants.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(1):34-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02199-08. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19828610 Free PMC article.
-
High density lipoprotein inhibits hepatitis C virus-neutralizing antibodies by stimulating cell entry via activation of the scavenger receptor BI.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 7;281(27):18285-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602706200. Epub 2006 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16675450
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I is a key host factor for hepatitis C virus infection required for an entry step closely linked to CD81.Hepatology. 2007 Dec;46(6):1722-31. doi: 10.1002/hep.21994. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 18000990
-
The scavenger receptor BI and its ligand, HDL: partners in crime against HCV neutralizing antibodies.J Viral Hepat. 2007 Nov;14 Suppl 1:68-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2007.00919.x. J Viral Hepat. 2007. PMID: 17958646 Review.
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I and the hypervariable region-1 of hepatitis C virus in cell entry and neutralisation.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2011 Apr 14;13:e13. doi: 10.1017/S1462399411001785. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21489334 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel small molecule inhibitor of hepatitis C virus entry.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Sep 2;6(9):e1001086. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001086. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20838466 Free PMC article.
-
HCV Interplay with Lipoproteins: Inside or Outside the Cells?Viruses. 2020 Apr 12;12(4):434. doi: 10.3390/v12040434. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32290553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hypervariable region 1 for the interplay of hepatitis C virus with entry factors and lipoproteins.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(21):12644-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01145-14. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25142595 Free PMC article.
-
CD81 and claudin 1 coreceptor association: role in hepatitis C virus entry.J Virol. 2008 May;82(10):5007-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02286-07. Epub 2008 Mar 12. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18337570 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibody to apolipoprotein A-1 in hepatitis C virus infection: a role in atherosclerosis?Hepatol Int. 2018 Jan;12(1):17-25. doi: 10.1007/s12072-018-9842-5. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Hepatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29423541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acton, S., A. Rigotti, K. T. Landschulz, S. Xu, H. H. Hobbs, and M. Krieger. 1996. Identification of scavenger receptor SR-BI as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science 271:518-520. - PubMed
-
- Barth, H., C. Schafer, M. I. Adah, F. Zhang, R. J. Linhardt, H. Toyoda, A. Kinoshita-Toyoda, T. Toida, T. H. Van Kuppevelt, E. Depla, F. Von Weizsacker, H. E. Blum, and T. F. Baumert. 2003. Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41003-41012. - PubMed
-
- Bartosch, B., A. Vitelli, C. Granire, C. Goujon, J. Dubuisson, S. Pascale, E. Scarselli, R., Cortese, A. Nicosia, and F. L. Cosset. 2003. Cell entry of hepatitis C virus requires a set of coreceptors that include the CD81 tetraspanin and the SR-B1 scavenger receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41624-41630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

