Arthritis suppression by NADPH activation operates through an interferon-beta pathway
- PMID: 17490473
- PMCID: PMC1884140
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-5-19
Arthritis suppression by NADPH activation operates through an interferon-beta pathway
Abstract
Background: A polymorphism in the activating component of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase complex, neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 (NCF1), has previously been identified as a regulator of arthritis severity in mice and rats. This discovery resulted in a search for NADPH oxidase-activating substances as a potential new approach to treat autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We have recently shown that compounds inducing NCF1-dependent oxidative burst, e.g. phytol, have a strong ameliorating effect on arthritis in rats. However, the underlying molecular mechanism is still not clearly understood. The aim of this study was to use gene-expression profiling to understand the protective effect against arthritis of activation of NADPH oxidase in the immune system.
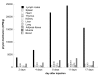
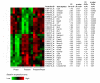
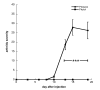
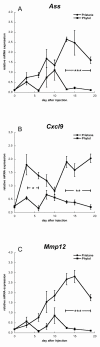
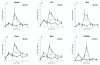
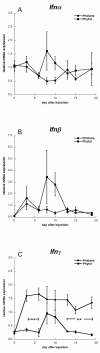
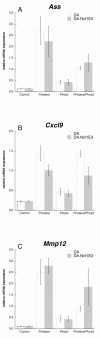
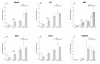
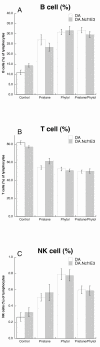
Results: Subcutaneous administration of phytol leads to an accumulation of the compound in the inguinal lymph nodes, with peak levels being reached approximately 10 days after administration. Hence, global gene-expression profiling on inguinal lymph nodes was performed 10 days after the induction of pristane-induced arthritis (PIA) and phytol administration. The differentially expressed genes could be divided into two pathways, consisting of genes regulated by different interferons. IFN-gamma regulated the pathway associated with arthritis development, whereas IFN-beta regulated the pathway associated with disease protection through phytol. Importantly, these two molecular pathways were also confirmed to differentiate between the arthritis-susceptible dark agouti (DA) rat, (with an Ncf-1DA allele that allows only low oxidative burst), and the arthritis-protected DA.Ncf-1E3 rat (with an Ncf1E3 allele that allows a stronger oxidative burst).
Conclusion: Naturally occurring genetic polymorphisms in the Ncf-1 gene modulate the activity of the NADPH oxidase complex, which strongly regulates the severity of arthritis. We now show that the Ncf-1 allele that enhances oxidative burst and protects against arthritis is operating through an IFN-beta-associated pathway, whereas the arthritis-driving allele operates through an IFN-gamma-associated pathway. Treatment of arthritis-susceptible rats with an NADPH oxidase-activating substance, phytol, protects against arthritis. Interestingly, the treatment led to a restoration of the oxidative-burst effect and induction of a strikingly similar IFN-beta-dependent pathway, as seen with the disease-protective Ncf1 polymorphism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced intercross line mapping suggests that ncf1 (ean6) regulates severity in an animal model of guillain-barre syndrome.J Immunol. 2009 Apr 1;182(7):4432-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803847. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19299744
-
A new arthritis therapy with oxidative burst inducers.PLoS Med. 2006 Sep;3(9):e348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030348. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 16968121 Free PMC article.
-
Positional identification of Ncf1 as a gene that regulates arthritis severity in rats.Nat Genet. 2003 Jan;33(1):25-32. doi: 10.1038/ng1058. Epub 2002 Dec 2. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 12461526
-
Ncf1 (p47phox) polymorphism determines oxidative burst and the severity of arthritis in rats and mice.Cell Immunol. 2005 Feb;233(2):97-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2005.04.008. Cell Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15936744 Review.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: the role of reactive oxygen species in disease development and therapeutic strategies.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007 Oct;9(10):1541-67. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1569. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007. PMID: 17678439 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive Oxygen Species in Autoimmune Cells: Function, Differentiation, and Metabolism.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:635021. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.635021. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Housekeeping gene stability in pristane-induced arthritis and antigen-induced pulmonary inflammation of rats.Inflamm Res. 2009 Sep;58(9):601-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-009-0027-5. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Inflamm Res. 2009. PMID: 19357809
-
Nox2 Deficiency Reduces Cartilage Damage and Ectopic Bone Formation in an Experimental Model for Osteoarthritis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 22;10(11):1660. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111660. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829531 Free PMC article.
-
VAMP8 Contributes to the TRIM6-Mediated Type I Interferon Antiviral Response during West Nile Virus Infection.J Virol. 2020 Jan 6;94(2):e01454-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01454-19. Print 2020 Jan 6. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694946 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary phytol reduces clinical symptoms in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) at least partially by modulating NOX2 expression.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Oct;96(10):1131-1144. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1689-7. Epub 2018 Aug 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30151738
References
-
- Symmons DP, Bankhead CR, Harrison BJ, Brennan P, Barrett EM, Scott DG, Silman AJ. Blood transfusion, smoking, and obesity as risk factors for the development of rheumatoid arthritis: results from a primary care-based incident case-control study in Norfolk, England. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1997;40:1955–1961. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401106. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bannwarth B, Labat L, Moride Y, Schaeverbeke T. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. An update. Drugs. 1994;47:25–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

