E2F1 death pathways as targets for cancer therapy
- PMID: 17488475
- PMCID: PMC3822825
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00030.x
E2F1 death pathways as targets for cancer therapy
Abstract
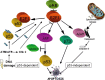
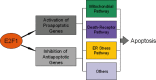
Defects in apoptotic programs contribute to a number of human diseases, ranging from neurodegenerative disorders to malignancy, and treatment failure. The genetic basis for apoptosis implies that cell death can be disrupted by mutations, raising the intriguing possibility that cell numbers can be regulated by factors that influence cell survival. It is well documented that the E2F1 transcription factor is a key regulator of apoptotic programs. E2F1-induced cell death occurs via multiple pathways, some of which involve the tumour suppressor p53, and autonomous of p53. This has led to the opinion that E2F1 functions as a tumour surveillance factor, detecting aberrant proliferation and engaging apoptotic pathways to protect the organism from developing tumours. Frequently, novel players are discovered that expand the interpretation of apoptosis control by E2F1. This information will help to produce new strategies to exploit E2F1-induced apoptosis for therapeutic benefit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Translating DNA damage into cancer cell death-A roadmap for E2F1 apoptotic signalling and opportunities for new drug combinations to overcome chemoresistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2010 Aug-Oct;13(4-5):119-31. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Aug 1. Drug Resist Updat. 2010. PMID: 20675184 Review.
-
The E2F1/Rb and p53/MDM2 pathways in DNA repair and apoptosis: understanding the crosstalk to develop novel strategies for prostate cancer radiotherapy.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010 Oct;20(4):258-66. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2010.05.007. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20832018 Review.
-
E2F1 apoptosis counterattacked: evil strikes back.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Feb;19(2):89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23219173 Review.
-
The E2F family and the role of E2F1 in apoptosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;41(12):2389-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19539777
-
EGFR signaling inhibits E2F1-induced apoptosis in vivo: implications for cancer therapy.Sci STKE. 2007 Jan 30;2007(371):pe4. doi: 10.1126/stke.3712007pe4. Sci STKE. 2007. PMID: 17264315
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs involved in tumor suppressor and oncogene pathways: implications for hepatobiliary neoplasia.Hepatology. 2009 Aug;50(2):630-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.23010. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19585622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major Molecular Signaling Pathways in Oral Cancer Associated With Therapeutic Resistance.Front Oral Health. 2021 Jan 25;1:603160. doi: 10.3389/froh.2020.603160. eCollection 2020. Front Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 35047986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional repression of the prosurvival endoplasmic reticulum chaperone GRP78/BIP by E2F1.J Biol Chem. 2008 Dec 5;283(49):34305-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803925200. Epub 2008 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18840615 Free PMC article.
-
The E2F activators control multiple mitotic regulators and maintain genomic integrity through Sgo1 and BubR1.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 8;8(44):77649-77672. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20765. eCollection 2017 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29100415 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis: a mapped path to cell death.J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Nov-Dec;11(6):1212-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00165.x. Epub 2007 Nov 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 18021308 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
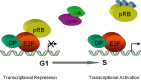
- Johnson DG, Schwarz JK, Cress WD, Nevins JR. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature. 1993;365:349–52. - PubMed
-
- Dyson N. The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2245–62. - PubMed
-
- Müller H, Helin K. The E2F transcription factors: key regulators of cell proliferration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1470:M1–2. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg RA. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995;81:323–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

