YbxF, a protein associated with exponential-phase ribosomes in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 17468242
- PMCID: PMC1913448
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01786-06
YbxF, a protein associated with exponential-phase ribosomes in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
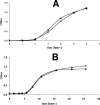
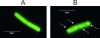
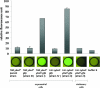
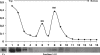
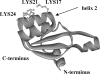
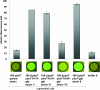
The ybxF gene is a member of the streptomycin operon in a wide range of gram-positive bacteria. In Bacillus subtilis, it codes for a small basic protein (82 amino acids, pI 9.51) of unknown function. We demonstrate that, in B. subtilis, YbxF localizes to the ribosome, primarily to the 50S subunit, with dependence on growth phase. Based on three-dimensional structures of YbxF generated by homology modeling, we identified helix 2 as important for the interaction with the ribosome. Subsequent mutational analysis of helix 2 revealed Lys24 as crucial for the interaction. Neither the B. subtilis ybxF gene nor its paralogue, the ymxC gene, is essential, as shown by probing DeltaybxF, DeltaymxC, or DeltaybxF DeltaymxC double deletion strains in several functional assays.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Towards an elucidation of the roles of the ribosome during different growth phases in Bacillus subtilis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(3):451-61. doi: 10.1271/bbb.90859. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20208344 Review.
-
Interaction between Bacillus subtilis YsxC and ribosomes (or rRNAs).FEBS Lett. 2015 Apr 13;589(9):1026-32. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 13. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 25771857
-
Specific polar localization of ribosomes in Bacillus subtilis depends on active transcription.EMBO Rep. 2001 Aug;2(8):685-9. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve160. Epub 2001 Jul 19. EMBO Rep. 2001. PMID: 11463749 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and interactions of teichoic acid synthetic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2008 Mar;190(5):1812-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.01394-07. Epub 2007 Dec 21. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18156271 Free PMC article.
-
Critical steps in the assembly process of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 8;52(8):4111-4123. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae199. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38554105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glioma Cells Acquire Stem-like Characters by Extrinsic Ribosome Stimuli.Cells. 2021 Nov 1;10(11):2970. doi: 10.3390/cells10112970. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831193 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome induces transdifferentiation of A549 and H-111-TC cancer cell lines.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Feb 12;26:100946. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100946. eCollection 2021 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 33644423 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome Incorporation into Somatic Cells Promotes Lineage Transdifferentiation towards Multipotency.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):1634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20057-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374279 Free PMC article.
-
Polar Fixation of Plasmids during Recombinant Protein Production in Bacillus megaterium Results in Population Heterogeneity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Sep 1;81(17):5976-86. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00807-15. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26116677 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular recognition of kink-turn structure by the L7Ae class of proteins.RNA. 2013 Dec;19(12):1703-10. doi: 10.1261/rna.041517.113. Epub 2013 Oct 22. RNA. 2013. PMID: 24149842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arndt, E., T. Scholzen, W. Kromer, T. Hatakeyama, and M. Kimura. 1991. Primary structures of ribosomal proteins from the archaebacterium Halobacterium marismortui and the eubacterium Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochimie 73:657-668. - PubMed
-
- Ban, N., P. Nissen, J. Hansen, P. B. Moore, and T. A. Steitz. 2000. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution. Science 289:905-920. - PubMed
-
- Chao, J. A., G. S. Prasad, S. A. White, C. D. Stout, and J. R. Williamson. 2003. Inherent protein structural flexibility at the RNA-binding interface of L30e. J. Mol. Biol. 326:999-1004. - PubMed
-
- Charron, C., X. Manival, B. Charpentier, C. Branlant, and A. Aubry. 2004. Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data of L7Ae sRNP core protein from Pyrococcus abyssii. Acta Crystallogr. D 60:122-124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

