Effects of mutant Drosophila K+ channel subunits on habituation of the olfactory jump response
- PMID: 17464797
- PMCID: PMC3045562
- DOI: 10.1080/01677060701247375
Effects of mutant Drosophila K+ channel subunits on habituation of the olfactory jump response
Abstract
The olfactory-jump response assay was used to analyze habituation in Drosophila mutants of potassium (K(+)) channel subunits. As with physiological assays of the giant fiber-mediated escape reflex, mutations at loci that encode K(+) channel subunits have distinct effects on habituating the olfactory-jump response. The data for slowpoke and ether à go-go indicate similar effects on habituation of the olfactory-jump response and the giant fiber-mediated escape. Habituation in the olfactory jump assay in Hyperkinetic and Shaker mutants was drastically different from the degree of defect in the giant fiber-mediated escape reflex, indicating differential control mechanisms underlying the two forms of non-associative conditioning.
Figures

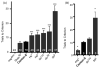
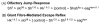
Similar articles
-
Neurogenetic approaches to habituation and dishabituation in Drosophila.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2009 Sep;92(2):166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2009. PMID: 18765288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory jump reflex habituation in Drosophila and effects of classical conditioning mutations.J Neurogenet. 2007 Jan-Jun;21(1-2):1-18. doi: 10.1080/01677060701247508. J Neurogenet. 2007. PMID: 17464794 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of functional contributions of specific potassium channel subunits in habituation of an escape circuit in Drosophila.J Neurosci. 1998 Mar 15;18(6):2254-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-06-02254.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9482810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced transmitter release conferred by mutations in the slowpoke-encoded Ca2(+)-activated K+ channel gene of Drosophila.Invert Neurosci. 1996 Jun;2(1):51-60. doi: 10.1007/BF02336660. Invert Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 9372155
-
The fickle mutation of a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase effects sensitization but not dishabituation in Drosophila melanogaster.J Neurogenet. 2007 Jan-Jun;21(1-2):59-71. doi: 10.1080/01677060701249488. J Neurogenet. 2007. PMID: 17464798 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Screening for Differentially Expressed Memory Genes on a Diabetes Model Induced by High-Sugar Diet in Drosophila melanogaster: Potential Markers for Memory Deficits.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Mar;61(3):1225-1236. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03598-z. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37698834
-
Accessing Olfactory Habituation in Drosophila melanogaster with a T-maze Paradigm.Bio Protoc. 2019 Jun 5;9(11):e3259. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3259. eCollection 2019 Jun 5. Bio Protoc. 2019. PMID: 33654781 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Regulation of Habituation Learning via Posttranslational Palmitoylation.Curr Biol. 2020 Jul 20;30(14):2729-2738.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.016. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32502414 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenetic approaches to habituation and dishabituation in Drosophila.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2009 Sep;92(2):166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2009. PMID: 18765288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microarray-based transcriptomic analysis of differences between long-term gregarious and solitarious desert locusts.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028110. Epub 2011 Nov 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22132225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelman J, Shen K, Kavanaugh M, Warren R, Wu Y, Lagrutta A, Bond C, North R. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 1992;9:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Allen M, Godenschwege T, Tanouye M, Phelan P. Making an escape: development and the function of the Drosophila giant fiber system. Semin Cell Devel Biol. 2006;17:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson N, Robertson G, Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991;253:551–555. - PubMed
-
- Bouhouche A, Vaysse G, Corbiere M. Immunocytochemical and learning studies of a Drosophila melanogaster neurological mutant, no-bridgeKS49 as an approach to the possible role of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. J Neurogenet. 1993;9:105–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
