Cholesterol-sensitive Cdc42 activation regulates actin polymerization for endocytosis via the GEEC pathway
- PMID: 17461795
- PMCID: PMC7617178
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00565.x
Cholesterol-sensitive Cdc42 activation regulates actin polymerization for endocytosis via the GEEC pathway
Abstract
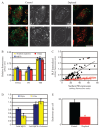
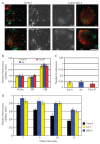
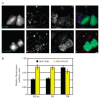
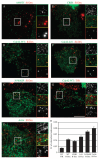
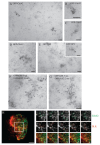
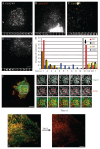
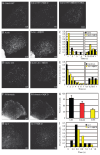
Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins (GPI-APs) are present at the surface of living cells in cholesterol dependent nanoscale clusters. These clusters appear to act as sorting signals for the selective endocytosis of GPI-APs via a Cdc42-regulated, dynamin and clathrin-independent pinocytic pathway called the GPI-AP-enriched early endosomal compartments (GEECs) pathway. Here we show that endocytosis via the GEECs pathway is inhibited by mild depletion of cholesterol, perturbation of actin polymerization or overexpression of the Cdc42/Rac-interactive-binding (CRIB) motif of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP). Consistent with the involvement of Cdc42-based actin nanomachinery, nascent endocytic vesicles containing cargo for the GEEC pathway co-localize with fluorescent protein-tagged isoforms of Cdc42, CRIB domain, N-WASP and actin; high-resolution electron microscopy on plasma membrane sheets reveals Cdc42-labelled regions rich in green fluorescent protein-GPI. Using total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy at the single-molecule scale, we find that mild cholesterol depletion alters the dynamics of actin polymerization at the cell surface by inhibiting Cdc42 activation and consequently its stabilization at the cell surface. These results suggest that endocytosis into GEECs occurs through a cholesterol-sensitive, Cdc42-based recruitment of the actin polymerization machinery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ARF1 is directly involved in dynamin-independent endocytosis.Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;10(1):30-41. doi: 10.1038/ncb1666. Epub 2007 Dec 16. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18084285 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01352-7 PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Spatially distinct binding of Cdc42 to PAK1 and N-WASP in breast carcinoma cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(5):1680-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.5.1680-1695.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15713627 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The architectural relationship of components controlling mast cell endocytosis.J Cell Sci. 2013 Nov 1;126(Pt 21):4913-25. doi: 10.1242/jcs.128876. Epub 2013 Aug 28. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23986485 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases, phosphoinositides, and actin: a tripartite framework for efficient vesicular trafficking.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29469. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29469. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24914539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the modeling of endocytosis in yeast.Biophys J. 2015 Feb 3;108(3):508-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3481. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25650919 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Heterogeneity Controls Cellular Endocytic Trafficking.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 5;8:757. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00757. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytic pathways involved in filovirus entry: advances, implications and future directions.Viruses. 2012 Dec;4(12):3647-64. doi: 10.3390/v4123647. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23342373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conner SD, Schmid SL. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature. 2003;422:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S, Ghosh RN, Maxfield FR. Endocytosis. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:759–803. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson J. Multiple roles for Arf6: Sorting, structuring and signaling at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:41573–41576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

