Upregulation of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha mRNA is associated with elevated vascular endothelial growth factor expression and excessive angiogenesis and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric carcinoma
- PMID: 17461470
- PMCID: PMC4146946
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i11.1680
Upregulation of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha mRNA is associated with elevated vascular endothelial growth factor expression and excessive angiogenesis and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the implication of the hypoxia inducible factor HIF-1alpha mRNA in gastric carcinoma and its relation to the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein, tumor angiogenesis invasion/metastasis and the patient's survival.
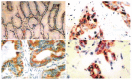
Methods: In situ hybridization was used to examine expression of HIF-1alpha mRNA, and immunohistochemical staining was used to examine expression of VEGF protein and CD34 in 118 specimens from patients with gastric carcinoma.
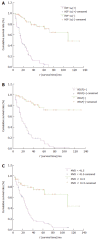
Results: The positive rates of HIF-1alpha mRNA and VEGF protein were 49.15% and 55.92%, respectively. Positive expressions of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in stage T3-T4 tumors and those with vessel invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis were dramatically stronger than stage T1-T2 cases and those without vessel invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis. The mean microvascular density (MVD) in stage T3-T4 tumors and those with vessel invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis was significantly higher than stage T1-T2 tumors and those without vessel invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis. The mean MVD in tumors with positive HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression was significantly higher than that in tumors with negative HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression. The expression of HIF-1alpha was positively correlated with VEGF protein. There were positive correlations between MVD and expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF. The mean survival time and the 5-year survival rate in cases with positive expression HIF-1alpha and VEGF and MVD value >or= 41.5/0.72 mm2 were significantly lower than those with negative expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF and MVD value < 41.5/0.72 mm2.
Conclusion: Overexpression of HIF-1alpha is found in gastric carcinoma. HIF-1alpha may induce the angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma by upregulating the transcription of VEGF gene, and take part in tumor invasion and metastasis. They can be used as prognostic markers of gastric cancer in clinical practice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Expressions of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and insulin-like growth factor-II in gastric carcinoma: correlation with angiogenesis and prognosis].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Jul 1;45(13):905-8. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17953839 Chinese.
-
[mRNA expression of IGF-IIand HGF in relation to microvascular density, tumor progression and prognosis of gastric carcinoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2004 Nov;26(11):673-7. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15777506 Chinese.
-
Correlative studies on uPA mRNA and uPAR mRNA expression with vascular endothelial growth factor, microvessel density, progression and survival time of patients with gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jul 7;12(25):3970-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i25.3970. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16810742 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and its clinical significance in lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Swiss Med Wkly. 2013 Sep 6;143:w13855. doi: 10.4414/smw.2013.13855. eCollection 2013. Swiss Med Wkly. 2013. PMID: 24018850 Review.
-
Critical role of hypoxia sensor--HIF-1α in VEGF gene activation. Implications for angiogenesis and tissue injury healing.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(1):90-7. doi: 10.2174/092986712803413944. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22300081 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric carcinoma: a meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011 Dec;137(12):1799-812. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1057-2. Epub 2011 Sep 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21918901
-
Co-expression and clinical utility of Snail and N-cadherin in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):413-7. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3820-5. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26219900
-
Radiofrequency ablation-induced upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α can be suppressed with adjuvant bortezomib or liposomal chemotherapy.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Dec;25(12):1972-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.08.025. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25439675 Free PMC article.
-
The HIF-1α as a Potent Inducer of the Hallmarks in Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 30;14(11):2711. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112711. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of HIF-1α expression in patients with gastric cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Nov;40(11):6055-62. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2715-z. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24057269 Review.
References
-
- Kaio E, Tanaka S, Kitadai Y, Sumii M, Yoshihara M, Haruma K, Chayama K. Clinical significance of angiogenic factor expression at the deepest invasive site of advanced colorectal carcinoma. Oncology. 2003;64:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Furudoi A, Tanaka S, Haruma K, Kitadai Y, Yoshihara M, Chayama K, Shimamoto F. Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor C expression and angiogenesis at the deepest invasive site of advanced colorectal carcinoma. Oncology. 2002;62:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Kondo Y, Hamada J, Kobayashi C, Nakamura R, Suzuki Y, Kimata R, Nishimura T, Kitagawa T, Kunimoto M, Imura N, et al. Over expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in renal and bladder cancer cells increases tumorigenic potency. J Urol. 2005;173:1762–1766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

