Phosphatidylinositol 3-Akt-kinase-dependent phosphorylation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) as a novel mechanism of neuroprotection by glucocorticoids
- PMID: 17460069
- PMCID: PMC6672985
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5110-06.2007
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Akt-kinase-dependent phosphorylation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) as a novel mechanism of neuroprotection by glucocorticoids
Abstract
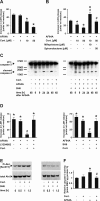
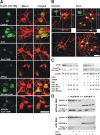
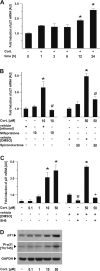
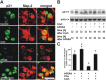
The role of glucocorticoids in the regulation of apoptosis remains incongruous. Here, we demonstrate that corticosterone protects neurons from apoptosis by a mechanism involving the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Waf1/Cip1). In primary cortical neurons, corticosterone leads to a dose- and Akt-kinase-dependent upregulation with enhanced phosphorylation and cytoplasmic appearance of p21(Waf1/Cip1) at Thr 145. Exposure of neurons to the neurotoxin ethylcholine aziridinium (AF64A) results in activation of caspase-3 and a dramatic loss of p21(Waf1/Cip1) preceding apoptosis in neurons. These effects of AF64A are reversed by pretreatment with corticosterone. Corticosterone-mediated upregulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) and neuroprotection are completely abolished by glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists as well as inhibitors of PI3- and Akt-kinase. Both germline and somatically induced p21(Waf1/Cip1) deficiency abrogate the neuroprotection by corticosterone, whereas overexpression of p21(Waf1/Cip1) suffices to protect neurons from apoptosis. We identify p21(Waf1/Cip1) as a novel antiapoptotic factor for postmitotic neurons and implicate p21(Waf1/Cip1) as the molecular target of neuroprotection by high-dose glucocorticoids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dose-response transition from cell cycle arrest to apoptosis with selective degradation of Mdm2 and p21WAF1/CIP1 in response to the novel anticancer agent, aminoflavone (NSC 686,288).Oncogene. 2007 Jul 19;26(33):4806-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210283. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17297446
-
Pulse inhibition of histone deacetylases induces complete resistance to oxidative death in cortical neurons without toxicity and reveals a role for cytoplasmic p21(waf1/cip1) in cell cycle-independent neuroprotection.J Neurosci. 2008 Jan 2;28(1):163-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3200-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18171934 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO target gene CTDSP2 regulates cell cycle progression through Ras and p21(Cip1/Waf1).Biochem J. 2015 Jul 15;469(2):289-98. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140831. Epub 2015 May 20. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25990325 Free PMC article.
-
p21Waf1/Cip1: its paradoxical effect in the regulation of breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2019 Mar;26(2):131-137. doi: 10.1007/s12282-018-0913-1. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Breast Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30255294 Review.
-
p21Cip1/Waf1 protein and its function based on a subcellular localization [corrected].J Cell Biochem. 2011 Dec;112(12):3502-6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23296. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21815189 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential role of interleukin-6 in post-stroke angiogenesis.Brain. 2012 Jun;135(Pt 6):1964-80. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws075. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Brain. 2012. PMID: 22492561 Free PMC article.
-
Unique pharmacological actions of atypical neuroleptic quetiapine: possible role in cell cycle/fate control.Transl Psychiatry. 2013 Apr 2;3(4):e243. doi: 10.1038/tp.2013.19. Transl Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23549417 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of ARC and Daxx: A Novel Endogenous Target to Preserve Motor Function and Cell Loss after Focal Brain Ischemia in Mice.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 3;36(31):8132-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4428-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27488634 Free PMC article.
-
Regional genome transcriptional response of adult mouse brain to hypoxia.BMC Genomics. 2011 Oct 11;12:499. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-499. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21988864 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Mouse and Human Studies Implicate ANGPT1 and ZBTB7C as Susceptibility Genes to Ischemic Injury.Stroke. 2015 Dec;46(12):3514-22. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010767. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Stroke. 2015. PMID: 26542693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ábrahám IM, Harkany T, Horvath KM, Luiten PGM. Action of glucocorticoids on survival of nerve cells: promoting neurodegeneration or neuroprotection? J Neuroendocrinol. 2001;13:749–760. - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam A, Tajima K, Sasson R. Cell-specific regulation of apoptosis by glucocorticoids. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64:843–850. - PubMed
-
- Bailly-Maitre B, de Sousa G, Boulukos K, Gugenheim J, Rahmani R. Dexamethasone inhibits spontaneous apoptosis in primary cultures of human and rat hepatocytes via Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL induction. Cell Death Differ. 2001;8:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Becker EB, Bonni A. Cell cycle regulation of neuronal apoptosis in development and disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2004;72:1–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
