Membrane topography of the hydrophobic anchor sequence of poliovirus 3A and 3AB proteins and the functional effect of 3A/3AB membrane association upon RNA replication
- PMID: 17417822
- PMCID: PMC2519882
- DOI: 10.1021/bi6024758
Membrane topography of the hydrophobic anchor sequence of poliovirus 3A and 3AB proteins and the functional effect of 3A/3AB membrane association upon RNA replication
Abstract
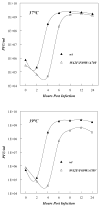
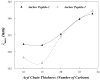
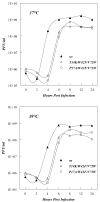
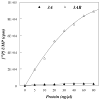
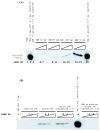
Replication of poliovirus RNA takes place on the cytoplasmic surface of membranous vesicles that form after infection of the host cell. It is generally accepted that RNA polymerase 3D(pol) interacts with membranes in a complex with viral protein 3AB, which binds to membranes by means of a hydrophobic anchor sequence that is located near the C-terminus of the 3A domain. In this study, we used fluorescence and fluorescence quenching methods to define the topography of the anchor sequence in the context of 3A and 3AB proteins inserted in model membranes. Mutants with a single tryptophan near the center of the anchor sequence but lacking Trp elsewhere in 3A/3AB were constructed which, after the emergence of suppressor mutations, replicated well in HeLa cells. When a peptide containing the mutant anchor sequence was incorporated in model membrane vesicles, measurements of Trp depth within the lipid bilayer indicated formation of a transmembrane topography. However, rather than the 22-residue length predicted from hydrophobicity considerations, the transmembrane segment had an effective length of 16 residues, such that Gln64 likely formed the N-terminal boundary. Analogous experiments using full-length proteins bound to preformed model membrane vesicles showed that the anchor sequence formed a mixture of transmembrane and nontransmembrane topographies in the 3A protein but adopted only the nontransmembrane configuration in the context of 3AB protein. Studies of the function of 3A/3AB inserted into model membrane vesicles showed that membrane-bound 3AB is highly efficient in stimulating the activity of 3D(pol) in vitro while membrane-bound 3A totally lacks this activity. Moreover, in vitro uridylylation reactions showed that membrane-bound 3AB is not a substrate for 3D(pol), but free VPg released by cleavage of 3AB with proteinase 3CD(pro) could be uridylylated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine 3 of poliovirus terminal peptide VPg(3B) has an essential function in RNA replication in the context of its precursor protein, 3AB.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5669-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02350-06. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17360746 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of protein-protein interactions critical for poliovirus replication: analysis of 3AB and VPg binding to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6369-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02252-06. Epub 2007 Apr 4. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17409142 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of protein domains of hepatitis A virus 3AB essential for interaction with 3CD and viral RNA.Virology. 1999 Nov 25;264(2):410-21. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.0017. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10562502
-
Uridylylation of the genome-linked protein of poliovirus in vitro is dependent upon an endogenous RNA template.Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):193-204. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90015-3. Virus Res. 1987. PMID: 2825442 Review.
-
Picornaviruses: A View from 3A.Viruses. 2021 Mar 11;13(3):456. doi: 10.3390/v13030456. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33799649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding knowledge of P3 proteins in the poliovirus lifecycle.Future Microbiol. 2010 Jun;5(6):867-81. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.40. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20521933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress on Functional Genomics Research of Enterovirus 71.Virol Sin. 2019 Feb;34(1):9-21. doi: 10.1007/s12250-018-0071-9. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Virol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30552635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of lipid composition on the topography of membrane-associated hydrophobic helices: stabilization of transmembrane topography by anionic lipids.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 13;379(4):704-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.026. Epub 2008 Apr 16. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18479706 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cationic Side Chains in the Antimicrobial Activity of C18G.Molecules. 2018 Feb 4;23(2):329. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020329. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29401708 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of protein-primed picornavirus RNA synthesis.Virus Res. 2015 Aug 3;206:12-26. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.12.028. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25592245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paul AV. Possible unifying mechanism of picornavirus genome replication. In: Semler BL, Wimmer E, editors. In molecular Biology of picornaviruses. ASM Press; Washington, DC: 2002. pp. 227–246.
-
- Bienz K, Egger D, Pasamontes L. Association of polioviral proteins of the P2 genomic region with the viral replication complex and virus-induced membrane synthesis as visualized by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry and autoradiography. Virology. 1987;160:220–226. - PubMed
-
- Egger D, Gosert R, Bienz K. Role of cellular structures in viral RNA replication. In: Semler BL, Wimmer E, editors. In Molecular Biology of Piocrnaviruses. ASM Press; Washington DC: 2002. pp. 20036–22904.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

