Target-specific PIP(2) signalling: how might it work?
- PMID: 17412762
- PMCID: PMC2075238
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.132787
Target-specific PIP(2) signalling: how might it work?
Abstract
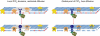
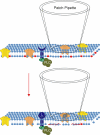
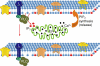
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2))-mediated signalling is a new and rapidly developing area in the field of cellular signal transduction. With the extensive and growing list of PIP(2)-sensitive membrane proteins (many of which are ion channels and transporters) and multiple signals affecting plasma membrane PIP(2) levels, the question arises as to the cellular mechanisms that confer specificity to PIP(2)-mediated signalling. In this review we critically consider two major hypotheses for such possible mechanisms: (i) clustering of PIP(2) in membrane microdomains with restricted lateral diffusion, a hypothesis providing a mechanism for spatial segregation of PIP(2) signals and (ii) receptor-specific buffering of the global plasma membrane PIP(2) pool via Ca(2+)-mediated stimulation of PIP(2) synthesis or release, a concept allowing for receptor-specific signalling with free lateral diffusion of PIP(2). We also discuss several other technical and conceptual intricacies of PIP(2)-mediated signalling.
Figures
Comment in
-
Role of PIP2 in regulating versus modulating Ca2+ channel activity.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 15;583(Pt 3):1165-6; author reply 1167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141424. Epub 2007 Aug 2. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17673503 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The complex and intriguing lives of PIP2 with ion channels and transporters.Sci STKE. 2001 Dec 4;2001(111):re19. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.111.re19. Sci STKE. 2001. PMID: 11734659 Review.
-
On the physiological roles of PIP(2) at cardiac Na+ Ca2+ exchangers and K(ATP) channels: a long journey from membrane biophysics into cell biology.J Physiol. 2007 Aug 1;582(Pt 3):903-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.132746. Epub 2007 Apr 26. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17463041 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive activation of K+ channel via phospholipase C-induced depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in B lymphocytes.J Physiol. 2007 Aug 1;582(Pt 3):977-90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.128413. Epub 2007 Mar 8. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17347270 Free PMC article.
-
Complex roles of PIP2 in the regulation of ion channels and transporters.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):F1761-5. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00400.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 10. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17928411 Review.
-
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate regulates epidermal growth factor receptor activation.Pflugers Arch. 2011 Mar;461(3):387-97. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0904-3. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Pflugers Arch. 2011. PMID: 21107857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) stimulates the electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransporter NBCe1-A expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 18;106(33):14150-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906303106. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19667194 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Segregation of Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate (PIP(2)) Signaling in Immune Cell Functions.Immunol Endocr Metab Agents Med Chem. 2008 Dec 1;8(4):349-357. doi: 10.2174/187152208787169233. Immunol Endocr Metab Agents Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 19956793 Free PMC article.
-
Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) properties and channelopathies.J Physiol. 2008 Apr 1;586(7):1785-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.148254. Epub 2008 Jan 3. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18174212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MARCKS protein plays a critical role in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism and directed cell movement in vascular endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 21;286(3):2320-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196022. Epub 2010 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21097841 Free PMC article.
-
SKF83959, an agonist of phosphatidylinositol-linked D(1)-like receptors, promotes ERK1/2 activation and cell migration in cultured rat astrocytes.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049954. Epub 2012 Nov 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992;71:713–716. - PubMed
-
- Arbuzova A, Murray D, McLaughlin S. MARCKS, membranes, and calmodulin: kinetics of their interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1376:369–379. - PubMed
-
- Balla T. Pharmacology of phosphoinositides, regulators of multiple cellular functions. Curr Pharm Des. 2001;7:475–507. - PubMed
-
- Bernheim L, Beech DJ, Hille B. A diffusible second messenger mediates one of the pathways coupling receptors to calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1991;6:859–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

