Solution structure of human sorting nexin 22
- PMID: 17400918
- PMCID: PMC2206652
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.072752407
Solution structure of human sorting nexin 22
Abstract
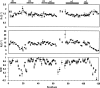
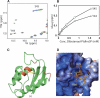
The sorting nexins (SNXs) constitute a large group of PX domain-containing proteins that play critical roles in protein trafficking. We report here the solution structure of human sorting nexin 22 (SNX22). Although SNX22 has <30% sequence identity with any PX domain protein of known structure, it was found to contain the alpha/beta fold and compact structural core characteristic of PX domains. Analysis of the backbone dynamics of SNX22 by NMR relaxation measurements revealed that the two walls of the ligand binding cleft undergo internal motions: on the picosecond timescale for the beta1/beta2 loop and on the micro- to millisecond timescale for the loop between the polyproline motif and helix alpha2. Regions of the SNX22 structure that differ from those of other PX domains include the loop connecting strands beta1 and beta2 and the loop connecting helices alpha1 and alpha2, which appear to be more mobile than corresponding loops in other known structures. The interaction of dibutanoyl-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (dibutanoyl-PtdIns(3)P) with SNX22 was investigated by an NMR titration experiment, which identified the binding site in a basic cleft and indicated that ligand binding leads only to a local structural rearrangement as has been found with other PX domains. Because motions in the loops are damped out when dibutanoyl-PtdIns(3)P binds, entropic effects could contribute to the lower affinity of SNX22 for this ligand compared to other PX domains.
Figures
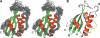

Similar articles
-
The phox domain of sorting nexin 5 lacks phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) specificity and preferentially binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2).J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 28;284(35):23697-707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.008995. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19553671 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of sorting nexin 17 domains and recognition motif for P-selectin trafficking.J Mol Biol. 2005 Apr 8;347(4):813-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.02.004. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15769472
-
The Phox (PX) domain proteins and membrane traffic.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1761(8):878-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.011. Epub 2006 May 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16782399 Review.
-
Sorting nexin homologues are targets of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in sporulation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Genes Cells. 2004 Jun;9(6):561-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00744.x. Genes Cells. 2004. PMID: 15189449
-
Sorting out the cellular functions of sorting nexins.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;3(12):919-31. doi: 10.1038/nrm974. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12461558 Review.
Cited by
-
The phox domain of sorting nexin 5 lacks phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) specificity and preferentially binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2).J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 28;284(35):23697-707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.008995. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19553671 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Phosphoinositide Code by Phosphorylation of Membrane Readers.Cells. 2021 May 14;10(5):1205. doi: 10.3390/cells10051205. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34069055 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositide Recognition Sites Are Blocked by Metabolite Attachment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 22;9:690461. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.690461. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34368138 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of sorting nexin 11 (SNX11) reveals a novel extended phox homology (PX) domain critical for inhibition of SNX10-induced vacuolation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16598-16605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.449306. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23615901 Free PMC article.
-
Neo-sex chromosomes in the black muntjac recapitulate incipient evolution of mammalian sex chromosomes.Genome Biol. 2008;9(6):R98. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-6-r98. Epub 2008 Jun 14. Genome Biol. 2008. PMID: 18554412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bravo J., Karathanassis, D., Pacold, C.M., Pacold, M.E., Ellson, C.D., Anderson, K.E., Butler, P.J., Lavenir, I., Perisic, O., Hawkins, P.T., et al. 2001. The crystal structure of the PX domain from p40(phox) bound to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Mol. Cell 8: 829–839. - PubMed
-
- Cheever M.L., Sato, T.K., de Beer, T., Kutateladze, T.G., Emr, S.D., and Overduin, M. 2001. Phox domain interaction with PtdIns(3)P targets the Vam7 t-SNARE to vacuole membranes. Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 613–618. - PubMed
-
- Cornilescu G., Delaglio, F., and Bax, A. 1999. Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J. Biomol. NMR 13: 289–302. - PubMed
-
- Delaglio F., Grzesiek, S., Vuister, G.W., Zhu, G., Pfeifer, J., and Bax, A. 1995. NMRPipe: A multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J. Biomol. NMR 6: 277–293. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez C., Boelens, R., and Bonvin, A.M. 2003. HADDOCK: A protein–protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125: 1731–1737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

