Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the lateral superior olive activate TRP-like channels: age- and experience-dependent regulation
- PMID: 17376850
- PMCID: PMC2322859
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00686.2006
Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the lateral superior olive activate TRP-like channels: age- and experience-dependent regulation
Abstract
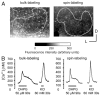
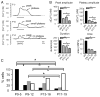
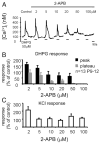
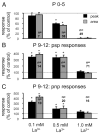
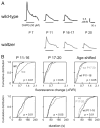
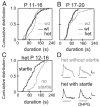
The lateral superior olive (LSO) is the primary auditory nucleus for processing of interaural sound level differences, which is one of the major cues for sound localization. During development, survival and maturation of LSO neurons critically depend on synaptic activity and intracellular calcium signaling. Before hearing onset, glutamatergic synaptic inputs from the cochlear nucleus (CN) to the LSO activate group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), which leads to calcium release from intracellular stores and large calcium influx from the extracellular milieu. Here, we investigated the nature of the mGluR-activated membrane channel that mediates the influx of extracellular calcium. Using Fura-2 calcium imaging in brain stem slices of neonatal and juvenile mice, we found that this calcium channel is blocked by Ni(2+), La(3+), and 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborane (2-APB), known antagonists of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. During postnatal development, the contribution of extracellular calcium influx to mGluR-mediated Ca(2+) responses gradually decreased and was almost abolished by the end of the third postnatal week. Over this period, the contribution of Ca(2+) release from internal stores remained unchanged. The developmental decrease of TRP-like channel-mediated calcium influx was significantly less in congenitally deaf waltzer mice, suggesting that early auditory experience is necessary for the normal age-dependent downregulation of functional TRP channels.
Figures
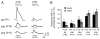
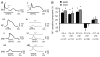
Similar articles
-
Glutamatergic calcium responses in the developing lateral superior olive: receptor types and their specific activation by synaptic activity patterns.J Neurophysiol. 2003 Oct;90(4):2581-91. doi: 10.1152/jn.00238.2003. Epub 2003 Jul 9. J Neurophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12853437
-
Glycinergic and GABAergic calcium responses in the developing lateral superior olive.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Apr;15(7):1093-104. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.01946.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11982621 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling routes and developmental regulation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat auditory midbrain neurons.J Neurosci Res. 2012 Oct;90(10):1913-23. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23087. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Neurosci Res. 2012. PMID: 22714707
-
Metabotropic receptor-activated calcium increases and store-operated calcium influx in mouse Müller cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Jul;49(7):3065-73. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1118. Epub 2008 Mar 3. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18316702
-
New Aspects of the Contribution of ER to SOCE Regulation: TRPC Proteins as a Link Between Plasma Membrane Ion Transport and Intracellular Ca2+ Stores.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;993:239-255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57732-6_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28900918 Review.
Cited by
-
Excitatory modulation in the cochlear nucleus through group I metabotropic glutamate receptor activation.J Neurosci. 2011 May 18;31(20):7450-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1193-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21593328 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and functional profiling of cell diversity and identity in the lateral superior olive, an auditory brainstem center with ascending and descending projections.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 May 23;18:1354520. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1354520. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38846638 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-Dependent Calcium Signaling in Neurons of the Medial Superior Olive during Late Postnatal Development.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 19;40(8):1689-1700. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1545-19.2020. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31949105 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperpolarization-independent maturation and refinement of GABA/glycinergic connections in the auditory brain stem.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Mar;115(3):1170-82. doi: 10.1152/jn.00926.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 9. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26655825 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of CaV3.2 channels enhances the arterial myogenic response by modulating the RyR-BKCa axis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Aug;35(8):1843-51. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305736. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26069238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Mackenzie L, Roderick HL, Berridge MJ, Peppiatt CM. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release. FASEB J. 2002;16:1145–1150. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau JC, Tsuchitani C. Binaural interaction in the cat superior olive S segment. J Neurophysiol. 1968;31:442–454. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29672–29680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

