Blockade of the 4-1BB (CD137)/4-1BBL and/or CD28/CD80/CD86 costimulatory pathways promotes corneal allograft survival in mice
- PMID: 17376197
- PMCID: PMC2265952
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02581.x
Blockade of the 4-1BB (CD137)/4-1BBL and/or CD28/CD80/CD86 costimulatory pathways promotes corneal allograft survival in mice
Abstract
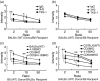
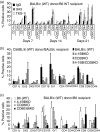
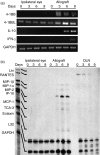
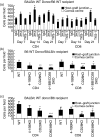
To explore the roles of 4-1BB (CD137) and CD28 in corneal transplantation, we examined the effect of 4-1BB/4-1BB ligand (4-1BBL) and/or CD28/CD80/CD86 blockade on corneal allograft survival in mice. Allogeneic corneal transplantation was performed between two strains of wild-type (WT) mice, BALB/c and C57BL/6 (B6), and between BALB/c and B6 WT donors and various gene knockout (KO) recipients. Some of the WT graft recipients were treated intraperitoneally with agonistic anti-4-1BB or blocking anti-4-1BBL monoclonal antibody (mAb) on days 0, 2, 4 and 6 after transplantation. Transplanted eyes were observed over a 13-week period. Allogeneic grafts in control WT B6 and BALB/c mice treated with rat immunoglobulin G showed median survival times (MST) of 12 and 14 days, respectively. Allogeneic grafts in B6 WT recipients treated with anti-4-1BB mAb showed accelerated rejection, with an MST of 8 days. In contrast, allogeneic grafts in BALB/c 4-1BB/CD28 KO and B6 CD80/CD86 KO recipients had significantly prolonged graft survival times (MST, 52.5 days and 36 days, respectively). Treatment of WT recipients with anti-4-1BB mAb resulted in enhanced cellular proliferation in the mixed lymphocyte reaction and increased the numbers of CD4(+) CD8(+) T cells, and macrophages in the grafts, which correlated with decreased graft survival time, whereas transplant recipients with costimulatory receptor deletion showed longer graft survival times. These results suggest that the absence of receptors for the 4-1BB/4-1BBL and/or CD28/CD80/CD86 costimulatory pathways promotes corneal allograft survival, whereas triggering 4-1BB with an agonistic mAb enhances the rejection of corneal allografts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of costimulation by CD28 and CD154 alters the kinetics and cellular characteristics of corneal allograft rejection.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Sep;44(9):3899-905. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-0084. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12939307
-
Blockade of 4-1BB (CD137)/4-1BB ligand interactions increases allograft survival.Transpl Int. 2004 Aug;17(7):351-61. doi: 10.1007/s00147-004-0726-3. Epub 2004 Jul 31. Transpl Int. 2004. PMID: 15349720
-
4-1BB (CD137) signals depend upon CD28 signals in alloimmune responses.Exp Mol Med. 2006 Dec 31;38(6):606-15. doi: 10.1038/emm.2006.72. Exp Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 17202836
-
Immunotherapy of cancer with 4-1BB.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 May;11(5):1062-70. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0677. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22532596 Review.
-
Dual immunoregulatory pathways of 4-1BB signaling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2006 Sep;84(9):726-36. doi: 10.1007/s00109-006-0072-2. Epub 2006 Aug 5. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16924475 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclosporine a drug-delivery system for high-risk penetrating keratoplasty: Stabilizing the intraocular immune microenvironment.PLoS One. 2018 May 7;13(5):e0196571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196571. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29734357 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of CD137 signaling counteracts polymicrobial sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture.Infect Immun. 2009 Sep;77(9):3932-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00407-09. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19564374 Free PMC article.
-
The role of costimulatory receptors of the tumour necrosis factor receptor family in atherosclerosis.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:464532. doi: 10.1155/2012/464532. Epub 2011 Dec 22. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22235167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of high-risk corneal transplantation.Surv Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov-Dec;62(6):816-827. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Surv Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28012874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Immune Checkpoint Molecules and Their Potential Role in the Transmissible Tasmanian Devil Facial Tumor Disease.Front Immunol. 2017 May 3;8:513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00513. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28515726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindstrom RL. Advances in corneal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1986;315:57–9. - PubMed
-
- Price FW, Jr, Whitson WE, Collins KS, Marks RG. Five-year corneal graft survival. A large, single-center patient cohort. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111:799–805. - PubMed
-
- Marrack P, Kappler J. The T cell receptor. Science. 1987;38:1073–9. - PubMed
-
- Comer RM, King WJ, Ardjomand N, Theoharis S, George AJ, Larkin DF. Effect of administration of CTLA4-Ig as protein or cDNA on corneal allograft survival. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:1095–103. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann F, Zhang EP, Pohl T, Kunzendorf U, Wachtlin J, Bulfone-Paus S. Inhibition of corneal allograft reaction by CTLA4-Ig. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1997;235:535–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

