The site-specific installation of methyl-lysine analogs into recombinant histones
- PMID: 17350582
- PMCID: PMC2932701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.041
The site-specific installation of methyl-lysine analogs into recombinant histones
Abstract
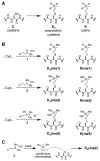
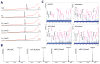
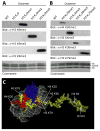
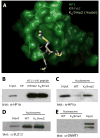
Histone lysine residues can be mono-, di-, or trimethylated. These posttranslational modifications regulate the affinity of effector proteins and may also impact chromatin structure independent of their role as adaptors. In order to study histone lysine methylation, particularly in the context of chromatin, we have developed a chemical approach to install analogs of methyl lysine into recombinant proteins. This approach allows for the rapid generation of large quantities of histones in which the site and degree of methylation can be specified. We demonstrate that these methyl-lysine analogs (MLAs) are functionally similar to their natural counterparts. These methylated histones were used to examine the influence of specific lysine methylation on the binding of effecter proteins and the rates of nucleosome remodeling. This simple method of introducing site-specific and degree-specific methylation into recombinant histones provides a powerful tool to investigate the biochemical mechanisms by which lysine methylation influences chromatin structure and function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Installation of site-specific methylation into histones using methyl lysine analogs.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2010 Apr;Chapter 21:Unit 21.18.1-10. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb2118s90. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20373501
-
A method to site-specifically incorporate methyl-lysine analogues into recombinant proteins.Methods Enzymol. 2012;512:57-69. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391940-3.00003-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22910202
-
The effect of H3K79 dimethylation and H4K20 trimethylation on nucleosome and chromatin structure.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Oct;15(10):1122-4. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1489. Epub 2008 Sep 14. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18794842 Free PMC article.
-
Towards understanding methyllysine readout.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1839(8):686-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24727128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The generation and recognition of histone methylation.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;41:25-46. doi: 10.1007/400_016. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 16909889 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of H3K9 methylation by GLP is required for efficient establishment of H3K9 methylation, rapid target gene repression, and mouse viability.Genes Dev. 2015 Feb 15;29(4):379-93. doi: 10.1101/gad.254425.114. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25637356 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of coregulators bound to ERα on DNA and nucleosomes reveals coregulator dynamics.Mol Cell. 2013 Jul 25;51(2):185-99. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23850489 Free PMC article.
-
Extending MeCP2 interactome: canonical nucleosomal histones interact with MeCP2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 24;52(7):3636-3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae051. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38321951 Free PMC article.
-
PHF20 is an effector protein of p53 double lysine methylation that stabilizes and activates p53.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;19(9):916-24. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2353. Epub 2012 Aug 5. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22864287 Free PMC article.
-
A variant NuRD complex containing PWWP2A/B excludes MBD2/3 to regulate transcription at active genes.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 18;9(1):3798. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06235-9. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30228260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chu F, Nusinow DA, Chalkley RJ, Plath K, Panning B, Burlingame AL. Mapping post-translational modifications of the histone variant MacroH2A1 using tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:194–203. - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove MS, Boeke JD, Wolberger C. Regulated nucleosome mobility and the histone code. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:1037–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

