Functional expression and microdomain localization of prestin in cultured cells
- PMID: 17321873
- PMCID: PMC2679365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.otohns.2006.10.030
Functional expression and microdomain localization of prestin in cultured cells
Abstract
Introduction: Prestin is an essential component of the molecular motor of cochlear outer hair cells that contribute to frequency selectivity and sensitivity of mammalian hearing. A model system to study prestin employs its transfection into cultured HEK 293 cells. Our goal was to characterize prestin's trafficking pathway and localization in the plasma membrane.
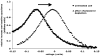
Methods: We used immuno-colocalization of prestin with intracellular and plasma membrane markers and sucrose density fractionation to analyze prestin in membrane compartments. Voltage clamping was used to measure nonlinear capacitance (NLC), prestin's electrical signature.
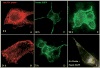
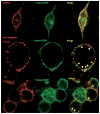
Results & discussion: Prestin targets to the membrane by 24 hours post-transfection when NLC is measurable. Prestin then concentrates into membrane foci that colocalize and fractionate with membrane microdomains. Depleting membrane cholesterol content altered prestin localization and NLC.
Conclusion: Prestin activity in HEK 293 cells results from expression in the plasma membrane and altering membrane lipid content affects prestin localization and activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glycosylation regulates prestin cellular activity.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2010 Mar;11(1):39-51. doi: 10.1007/s10162-009-0196-5. Epub 2009 Nov 7. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2010. PMID: 19898896 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminus of prestin influences nonlinear capacitance and plasma membrane targeting.J Cell Sci. 2005 Jul 1;118(Pt 13):2987-96. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02431. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15976456
-
Maturation of Voltage-induced Shifts in SLC26a5 (Prestin) Operating Point during Trafficking and Membrane Insertion.Neuroscience. 2020 Apr 1;431:128-133. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.02.003. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Neuroscience. 2020. PMID: 32061780 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in understanding the structural mechanism underlying prestin's electromotile activity.Hear Res. 2022 Sep 15;423:108423. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2021.108423. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Hear Res. 2022. PMID: 34987017 Review.
-
Intracellular cholesterol transport.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 Jul;24(7):1150-60. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000131264.66417.d5. Epub 2004 May 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15130918 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional prestin transduction of immature outer hair cells from normal and prestin-null mice.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2008 Sep;9(3):307-20. doi: 10.1007/s10162-008-0121-3. Epub 2008 May 28. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2008. PMID: 18506528 Free PMC article.
-
Real time measures of prestin charge and fluorescence during plasma membrane trafficking reveal sub-tetrameric activity.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 10;8(6):e66078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066078. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762468 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane composition modulates prestin-associated charge movement.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 15;283(33):22473-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803722200. Epub 2008 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18567583 Free PMC article.
-
Outer Hair Cell Lateral Wall Structure Constrains the Mobility of Plasma Membrane Proteins.PLoS Genet. 2015 Sep 9;11(9):e1005500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005500. eCollection 2015 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26352669 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral wall protein content mediates alterations in cochlear outer hair cell mechanics before and after hearing onset.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007 Sep;64(9):705-17. doi: 10.1002/cm.20217. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007. PMID: 17615570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng J, Shen W, He DZ, et al. Prestin is the motor protein of cochlear outer hair cells. Nature. 2000;405:149–55. - PubMed
-
- Adler HJ, Belyantseva IA, Merritt RCJ, et al. Expression of prestin, a membrane motor protein, in the mammalian auditory and vestibular periphery. Hear Res. 2003;184:27–40. - PubMed
-
- Zheng J, Long KB, Shen W, et al. Prestin topology: localization of protein epitopes in relation to the plasma membrane. Neuroreport. 2001;12:1929–35. - PubMed
-
- Brownell WE. The piezoelectric outer hair cell. In: Eatock RA, Popper AN, Fay RR, editors. Vertibrate Hair Cells. Springer; NY: 2006. pp. 313–347. In the Springer Handbook of Auditory Research.
-
- Dallos P, Fakler B. Prestin, a new type of motor protein. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:104–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

