Prediction of supertype-specific HLA class I binding peptides using support vector machines
- PMID: 17303158
- PMCID: PMC2806231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.12.011
Prediction of supertype-specific HLA class I binding peptides using support vector machines
Abstract
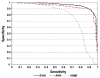
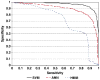
Experimental approaches for identifying T-cell epitopes are time-consuming, costly and not applicable to the large scale screening. Computer modeling methods can help to minimize the number of experiments required, enable a systematic scanning for candidate major histocompatibility complex (MHC) binding peptides and thus speed up vaccine development. We developed a prediction system based on a novel data representation of peptide/MHC interaction and support vector machines (SVM) for prediction of peptides that promiscuously bind to multiple Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA, human MHC) alleles belonging to a HLA supertype. Ten-fold cross-validation results showed that the overall performance of SVM models is improved in comparison to our previously published methods based on hidden Markov models (HMM) and artificial neural networks (ANN), also confirmed by blind testing. At specificity 0.90, sensitivity values of SVM models were 0.90 and 0.92 for HLA-A2 and -A3 dataset respectively. Average area under the receiver operating curve (A(ROC)) of SVM models in blind testing are 0.89 and 0.92 for HLA-A2 and -A3 datasets. A(ROC) of HLA-A2 and -A3 SVM models were 0.94 and 0.95, validated using a full overlapping study of 9-mer peptides from human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 proteins. In addition, a large-scale experimental dataset has been used to validate HLA-A2 and -A3 SVM models. The SVM prediction models were integrated into a web-based computational system MULTIPRED1, accessible at antigen.i2r.a-star.edu.sg/multipred1/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MULTIPRED: a computational system for prediction of promiscuous HLA binding peptides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W172-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki452. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980449 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of class I T-cell epitopes: evidence of presence of immunological hot spots inside antigens.Bioinformatics. 2004 Aug 4;20 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i297-302. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth943. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15262812 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the prediction of HLA class I-binding peptides using a supertype-based method.J Immunol Methods. 2014 Mar;405:109-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.01.015. Epub 2014 Feb 6. J Immunol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24508661
-
Class I MHC-peptide interaction: structural and functional aspects.Behring Inst Mitt. 1994 Jul;(94):48-60. Behring Inst Mitt. 1994. PMID: 7998914 Review.
-
Virtual models of the HLA class I antigen processing pathway.Methods. 2004 Dec;34(4):429-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2004.06.005. Methods. 2004. PMID: 15542368 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of MHC-II peptide binding prediction servers: applications for vaccine research.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Dec 12;9 Suppl 12(Suppl 12):S22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-S12-S22. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 19091022 Free PMC article.
-
MULTiPly: a novel multi-layer predictor for discovering general and specific types of promoters.Bioinformatics. 2019 Sep 1;35(17):2957-2965. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz016. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30649179 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of MHC class I peptide binding prediction servers: applications for vaccine research.BMC Immunol. 2008 Mar 16;9:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-8. BMC Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18366636 Free PMC article.
-
Hotspot Hunter: a computational system for large-scale screening and selection of candidate immunological hotspots in pathogen proteomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-S1-S19. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18315850 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Methods for Predicting HLA-Peptide Binding Activity.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2015 Oct 11;9(Suppl 3):21-9. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S29466. eCollection 2015. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2015. PMID: 26512199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander C, Kay AB, Larche M. Peptide-based vaccines in the treatment of specific allergy. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002;1:353. - PubMed
-
- Antes I, Siu SW, Lengauer T. DynaPred: a structure and sequence based method for the prediction of MHC class I binding peptide sequences and conformations. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:e16. - PubMed
-
- Berzofsky JA, Ahlers JD, Belyakov IM. Strategies for designing and optimizing new generation vaccines. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:209. - PubMed
-
- Bhasin M, Raghava GP. Prediction of CTL epitopes using QM, SVM and ANN techniques. Vaccine. 2004;22:3195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous