XRCC4:DNA ligase IV can ligate incompatible DNA ends and can ligate across gaps
- PMID: 17290226
- PMCID: PMC1852838
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601559
XRCC4:DNA ligase IV can ligate incompatible DNA ends and can ligate across gaps
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2007 Jul 25;26(14):3506-7
Abstract
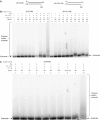
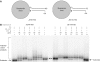
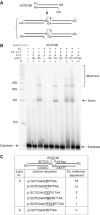
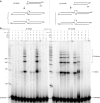
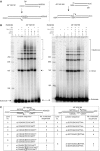
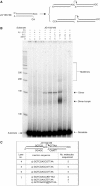
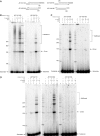
XRCC4 and DNA ligase IV form a complex that is essential for the repair of all double-strand DNA breaks by the nonhomologous DNA end joining pathway in eukaryotes. We find here that human XRCC4:DNA ligase IV can ligate two double-strand DNA ends that have fully incompatible short 3' overhang configurations with no potential for base pairing. Moreover, at DNA ends that share 1-4 annealed base pairs, XRCC4:DNA ligase IV can ligate across gaps of 1 nt. Ku can stimulate the joining, but is not essential when there is some terminal annealing. Polymerase mu can add nucleotides in a template-independent manner under physiological conditions; and the subset of ends that thereby gain some terminal microhomology can then be ligated. Hence, annealing at sites of microhomology is very important, but the flexibility of the ligase complex is paramount in nonhomologous DNA end joining. These observations provide an explanation for several in vivo observations that were difficult to understand previously.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-stranded DNA ligation and XLF-stimulated incompatible DNA end ligation by the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex: influence of terminal DNA sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(17):5755-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm579. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17717001 Free PMC article.
-
C-Terminal region of DNA ligase IV drives XRCC4/DNA ligase IV complex to chromatin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Sep 20;439(2):173-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.068. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23994631
-
Ku recruits the XRCC4-ligase IV complex to DNA ends.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(9):2996-3003. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.9.2996-3003.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10757784 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC4 and XLF form long helical protein filaments suitable for DNA end protection and alignment to facilitate DNA double strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):31-41. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0058. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flexibility in the order of action and in the enzymology of the nuclease, polymerases, and ligase of vertebrate non-homologous DNA end joining: relevance to cancer, aging, and the immune system.Cell Res. 2008 Jan;18(1):125-33. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.108. Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18087292 Review.
Cited by
-
Repair of double-strand breaks by end joining.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 May 1;5(5):a012757. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012757. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23637284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymerase δ promotes chromosomal rearrangements and imprecise double-strand break repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 3;117(44):27566-27577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014176117. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33077594 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular basis and disease relevance of non-homologous DNA end joining.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Dec;21(12):765-781. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00297-8. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33077885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limiting the persistence of a chromosome break diminishes its mutagenic potential.PLoS Genet. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000683. Epub 2009 Oct 16. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19834534 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative end-joining is suppressed by the canonical NHEJ component Xrcc4-ligase IV during chromosomal translocation formation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Apr;17(4):410-6. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1773. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20208544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP (2006) XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote nonhomologous end-joining. Cell 124: 301–313 - PubMed
-
- Bertocci B, DeSmet A, Weill J-C, Reynaud CA (2006) Non-overlapping functions of polX family DNA polymerases, pol μ, pol λ, and TdT, during immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination in vivo. Immunity 25: 31–41 - PubMed
-
- Bertocci B, Smet AD, Berek C, Weill J-C, Reynaud C-A (2003) Immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene rearrangement is impaired in mice deficient for DNA polymerase mu. Immunity 19: 203–211 - PubMed
-
- Buck D, Malivert L, deChasseval R, Barraud A, Fondaneche M-C, Xanal O, Plebani A, Stephan J-L, Hufnagel M, LeDiest F, Fischer A, Durrandy A, Villartay J-Pd, Revy P (2006) Cernunnos, a novel nonhomologous end-joining factor, is mutated in human immunodeficiency with microcephaly. Cell 124: 287–299 - PubMed
-
- Callebaut I, Malivert L, Fischer A, Mornon JP, Revy P, Villartay JPd (2006) Cernunnos interacts with the XRCC4/DNA-ligase IV complex and is homologous to the yeast nonhomologous end-joining factor NEJ1. J Biol Chem 281: 13857–13860 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

