The low-toxicity 9-cis UAB30 novel retinoid down-regulates the DNA methyltransferases and has anti-telomerase activity in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 17273765
- PMCID: PMC2435481
The low-toxicity 9-cis UAB30 novel retinoid down-regulates the DNA methyltransferases and has anti-telomerase activity in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
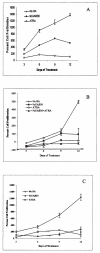
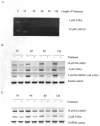
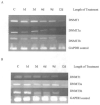
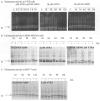
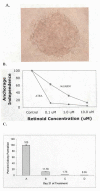
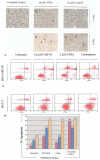
Retinoic acids and their derivatives potentiate anti-cancer effects in breast cancer cells. The aberrant expression of telomerase is critical to the continued proliferation of most cancer cells. Thus, telomerase is an attractive target for chemoprevention and treatment of breast cancer. 9cUAB30 is a novel synthetic retinoid X receptor-selective retinoic acid (RA) that effectively reduces the tumorigenic phenotype in mouse breast carcinoma with lower toxic effects than natural retinoid treatments. We have assessed 9cUAB30 retinoic acid treatment of human breast cancer cells to determine the potential of this drug as an effective telomerase inhibitor and its application to cancer therapy. 9cUAB30 was found to decrease DNA methyltransferase and telomerase expression in MDA-MB-361, T-47D, and MCF-7 human breast cancer cells and to inhibit the proliferation of these cells. This low-toxicity retinoid also reduced colony formation in soft agar assays in each of these cell types. Combination treatments of 9cUAB30 and all-trans RA proved to be synergistically more effective than either RA alone, further suggesting a possible general epigenetic mechanism that contributes to the anti-telomerase activity of the retinoids. Therefore, the novel retinoid, 9cUAB30, is effective in inhibiting the growth of human breast cancer cells, its anti-cancer effects appear to be related to telomerase inhibition and the mechanism for this process could be mediated through epigenetic modifications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulation of telomerase in retinoid-induced differentiation of human leukemia cells.Int J Oncol. 2008 Mar;32(3):625-31. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18292940 Free PMC article.
-
9-Cis retinoic acid inhibits growth of breast cancer cells and down-regulates estrogen receptor RNA and protein.Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6549-56. Cancer Res. 1994. PMID: 7987855
-
EGCG down-regulates telomerase in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells, leading to suppression of cell viability and induction of apoptosis.Int J Oncol. 2004 Mar;24(3):703-10. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14767556
-
A novel all-trans retinoid acid derivatives inhibits the migration of breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 via myosin light chain kinase involving p38-MAPK pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2013 Jun;67(5):357-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2013.03.016. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23602051
-
Translation of a Tissue-Selective Rexinoid, UAB30, to the Clinic for Breast Cancer Prevention.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(6):676-695. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160617093604. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27320329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel retinoid X receptor agonist, UAB30, inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma cells in vitro.J Surg Res. 2018 Aug;228:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.02.057. Epub 2018 Mar 26. J Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 29907230 Free PMC article.
-
An Isochroman Analog of CD3254 and Allyl-, Isochroman-Analogs of NEt-TMN Prove to Be More Potent Retinoid-X-Receptor (RXR) Selective Agonists Than Bexarotene.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 19;23(24):16213. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416213. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555852 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid-induced histone deacetylation inhibits telomerase activity in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2009 Dec;29(12):4959-64. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 20044602 Free PMC article.
-
Micronutrient status and global DNA methylation in school-age children.Epigenetics. 2012 Oct;7(10):1133-41. doi: 10.4161/epi.21915. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22918385 Free PMC article.
-
The retinoid X receptor has a critical role in synthetic rexinoid-induced increase in cellular all-trans-retinoic acid.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 1;19(4):e0301447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301447. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38557762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kelland LR. Overcoming the immortality of tumor cells by telomere and telomerase based cancer therapeutics - current status and future prospects. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:971–979. - PubMed
-
- Gudas L. Retinoids and vertebrate development. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:15399–15402. - PubMed
-
- Choi SH, Kang HK, Im EO, et al. Inhibition of cell growth and telomerase activity in breast cancer cells in vitro by retinoic acids. Int J Oncol. 2000;17:971–976. - PubMed
-
- Dedieu S, Lefebvre P. Retinoids interfere with the AP1 signalling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2006;18:889–898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

