c-Myc primed mitochondria determine cellular sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 17268552
- PMCID: PMC1852827
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601551
c-Myc primed mitochondria determine cellular sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis
Abstract
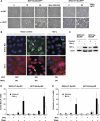
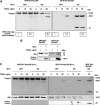
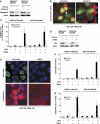
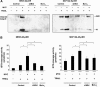
Oncogenic c-Myc renders cells sensitive to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, and existing data suggest that c-Myc sensitizes cells to apoptosis by promoting activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. However, the molecular mechanisms linking the mitochondrial effects of c-Myc to the c-Myc-dependent sensitization to TRAIL have remained unresolved. Here, we show that TRAIL induces a weak activation of procaspase-8 but fails to activate mitochondrial proapoptotic effectors Bax and Bak, cytochrome c release or downstream effector caspase-3 in non-transformed human fibroblasts or mammary epithelial cells. Our data is consistent with the model that activation of oncogenic c-Myc primes mitochondria through a mechanism involving activation of Bak and this priming enables weak TRAIL-induced caspase-8 signals to activate Bax. This results in cytochrome c release, activation of downstream caspases and postmitochondrial death-inducing signaling complex -independent augmentation of caspase-8-Bid activity. In conclusion, c-Myc-dependent priming of the mitochondrial pathway is critical for the capacity of TRAIL-induced caspase-8 signals to activate effector caspases and for the establishment of lethal caspase feedback amplification loop in human cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced mitochondrial disruption and apoptosis: differential regulation of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release.Cancer Res. 2003 Apr 1;63(7):1712-21. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12670926
-
Reactive oxygen species regulate caspase activation in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-resistant human colon carcinoma cell lines.Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 15;65(16):7436-45. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2628. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16103097
-
Oxaliplatin sensitizes human colon cancer cells to TRAIL through JNK-dependent phosphorylation of Bcl-xL.Gastroenterology. 2011 Aug;141(2):663-73. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.055. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21683075
-
c-Myc blazing a trail of death: coupling of the mitochondrial and death receptor apoptosis pathways by c-Myc.Cell Cycle. 2007 Oct 15;6(20):2464-72. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.20.4917. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17914284 Review.
-
Sensitization of melanoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis by activation of mitochondrial pathways via Bax.Eur J Cell Biol. 2014 Jan-Feb;93(1-2):42-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 23. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24361324 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the intrinsic but not the extrinsic apoptosis pathway accelerates and drives MYC-driven tumorigenesis towards acute myeloid leukemia.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031366. Epub 2012 Feb 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22393362 Free PMC article.
-
Myc requires RhoA/SRF to reprogram glutamine metabolism.Small GTPases. 2018 May 4;9(3):274-282. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1224287. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 27532209 Free PMC article.
-
Cell senescence-associated genes predict the malignant characteristics of glioblastoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 16;22(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02834-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36527013 Free PMC article.
-
Serine 62-Phosphorylated MYC Associates with Nuclear Lamins and Its Regulation by CIP2A Is Essential for Regenerative Proliferation.Cell Rep. 2015 Aug 11;12(6):1019-31. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26235622 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis regulation in adrenocortical carcinoma.Endocr Connect. 2019 May 1;8(5):R91-R104. doi: 10.1530/EC-19-0114. Endocr Connect. 2019. PMID: 30978697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Algeciras-Schimnich A, Barnhart BC, Peter ME (2002) Apoptosis-independent functions of killer caspases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14: 721–726 - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Cooper CL, Wagner K, Batalov S, Deveraux QL, Cooke MP (2003) Identification of modulators of TRAIL-induced apoptosis via RNAi-based phenotypic screening. Mol Cell 12: 627–637 - PubMed
-
- Boatright KM, Renatus M, Scott FL, Sperandio S, Shin H, Pedersen IM, Ricci JE, Edris WA, Sutherlin DP, Green DR, Salvesen GS (2003) A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol Cell 11: 529–541 - PubMed
-
- Certo M, Moore Vdel G, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA, Letai A (2006) Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 9: 351–365 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

