CD8 apoptosis may be a predictor of T cell number normalization after immune reconstitution in HIV
- PMID: 17263884
- PMCID: PMC1800849
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-5-9
CD8 apoptosis may be a predictor of T cell number normalization after immune reconstitution in HIV
Abstract
Background: As part of the Houston Vanguard study, a subset of 10 patients randomized to receive IL-2 therapy were compared to 4 patients randomized to not receive IL-2, for markers of T cell activation and death during the first three cycles of IL-2. All patients were treated with combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) and were virally suppressed. The purpose of the study was to examine the role of CD8(+) T cell death in responses to ART and IL-2 therapy.
Methods: Lymphocytes were examined at Day 0, 5 and 30 days during three cycles of IL-2 therapy. CD25, CD38, HLA-DR expression and annexin (cell death) were examined on CD4 and CD8 subpopulations. Follow up studies examined CD4 levels and CD4:CD8 reconstitution after 6 years using both univariant and multivariate analyses.
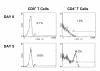
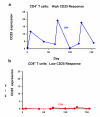
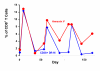
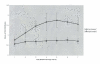
Results: Human lymphocytes responded to IL-2 therapy by upregulation of CD25 on CD4(+) T cells, leading to an increase in CD4 cell counts. CD8(+) T cells did not increase CD25 expression, but upregulated activation antigens (CD38 and DR) and had increased death. At baseline, 7 of the 14 patients had high CD8+ T cell apoptosis (mean 17.0% +/- 6.0). We did an exploratory analysis of immune status after six years, and found that baseline CD8+ T cell apoptosis was correlated with CD4 cell count gain beginning two years post enrollment. Patients with low levels of CD8(+) T cell apoptosis at baseline (mean 2.2% +/- 2.1) had significantly higher CD4 cell counts and more normalized CD4:CD8 ratios than patients with high CD8(+) T cell apoptosis (mean CD4 cell counts 1,209 +/- 164 vs 754 +/- 320 cells/mm(3); CD4:CD8 ratios 1.55 vs. 0.70, respectively).
Conclusion: We postulate that CD8(+) T cell apoptosis may reflect inherent activation status, which continues in some patients even though viral replication is suppressed which influences the ability of CD4(+) T cells to rebound. Levels of CD8(+) T cell apoptosis may therefore be an independent predictor of immune status, which should be shown in a prospective study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of intermittent interleukin-2 therapy on CD4+ T-cell counts following antiretroviral cessation in patients with HIV.AIDS. 2012 Mar 27;26(6):711-20. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283519214. AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22301410 Clinical Trial.
-
CD38+CD8+ T-cells negatively correlate with CD4 central memory cells in virally suppressed HIV-1-infected individuals.AIDS. 2008 Oct 1;22(15):1937-41. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32830f97e2. AIDS. 2008. PMID: 18784457
-
Close association of CD8+/CD38 bright with HIV-1 replication and complex relationship with CD4+ T-cell count.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2009 Jul;76(4):249-60. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.20467. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2009. PMID: 19072838
-
CD4+ lymphocyte increases in HIV patients during potent antiretroviral therapy are dependent on inhibition of CD8+ cell apoptosis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Dec;1010:560-4. doi: 10.1196/annals.1299.104. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 15033791 Review.
-
The role of interleukin-21 in HIV infection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012 Aug-Oct;23(4-5):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012. PMID: 22763176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD56dim NK Cell is an Important Factor in T Cell Depletion of cART-Treated AIDS Patients.Int J Gen Med. 2022 May 3;15:4575-4583. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S356771. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35535146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sereti I, Anthony KB, Martinez-Wilson H, Lempicki R, Adelsberger J, Metcalf JA, Hallahan CW, Follmann D, Davey RT, Kovacs JA, Lane C. IL-2-induced CD4+ T-cell expansion in HIV-infected patients is associated with long-term decreases in T-cell proliferation. Blood. 2004;104:775–780. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4355. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kovacs JA, Lempicki RA, Sidorov I, Adelsberger JW, Sereti I, Sachau W, Nelly G, Metcalf JA, Davey RT, Falloon J, Polis MA, Tavel J, Stevens R, Lambert L, Hosack DA, Bosche M, Isaac HJ, Fox SD, Leitman S, Baseler MW, Masur H, Di Mascio M, Dimitrov DS, Lane HC. Induction of prolonged survival of CD4+ T lymphocytes by intermittent IL-2 therapy in HIV-infected patients. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2139–2148. doi: 10.1172/JCI23196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seriti I, Imamichi H, Natarajan V, Imamichi T, Ramchandani MS, Badralmaa Y, Berg SC, Metcalf JA, Hahn BK, Shen JM, Powers A, Davey RT, Kovacs JA, Shevach EM, Lane HC. In vivo expansion of CD4+ CD45RO-CD25+ T cells expressing foxP3 in IL-2-treated HIV-infected patients. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1839–1847. doi: 10.1172/JCI24307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

