Growth factor independence-1 (Gfi-1) plays a role in mediating specific granule deficiency (SGD) in a patient lacking a gene-inactivating mutation in the C/EBPepsilon gene
- PMID: 17244686
- PMCID: PMC1885490
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-022004
Growth factor independence-1 (Gfi-1) plays a role in mediating specific granule deficiency (SGD) in a patient lacking a gene-inactivating mutation in the C/EBPepsilon gene
Abstract
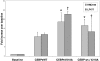
Neutrophil-specific granule deficiency (SGD) is a rare congenital disorder marked by recurrent bacterial infections. Neutrophils from SGD patients lack secondary and tertiary granules and their content proteins and lack normal neutrophil functions. Gene-inactivating mutations in the C/EBPepsilon gene have been identified in 2 SGD patients. Our studies on a third SGD patient revealed a heterozygous mutation in the C/EBPepsilon gene. However, we demonstrate elevated levels of C/EBPepsilon and PU.1 proteins in the patient's peripheral blood neutrophils. The expression of the transcription factor growth factor independence-1 (Gfi-1), however, was found to be markedly reduced in our SGD patient despite the absence of an obvious mutation in this gene. This may explain the elevated levels of both C/EBPepsilon and PU.1, which are targets of Gfi-1 transcriptional repression. We have generated a growth factor-dependent EML cell line from the bone marrow of Gfi-1(+/-) and Gfi-1(+/+) mice as a model for Gfi-1-deficient SGD, and demonstrate that lower levels of Gfi-1 expression in the Gfi-1(+/-) EML cells is associated with reduced levels of secondary granule protein (SGP) gene expression. Furthermore, we demonstrate a positive role for Gfi-1 in SGP expression, in that Gfi-1 binds to and up-regulates the promoter of neutrophil collagenase (an SGP gene), in cooperation with wild-type but not with mutant C/EBPepsilon. We hypothesize that decreased Gfi-1 levels in our SGD patient, together with the mutant C/EBPepsilon, block SGP expression, thereby contributing to the underlying etiology of the disease in our patient.
Figures

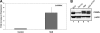
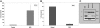

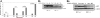

Similar articles
-
A Novel In-Frame Deletion in the Leucine Zipper Domain of C/EBPε Leads to Neutrophil-Specific Granule Deficiency.J Immunol. 2015 Jul 1;195(1):80-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402222. Epub 2015 May 27. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26019275
-
Neutrophil-specific granule deficiency: homozygous recessive inheritance of a frameshift mutation in the gene encoding transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein--epsilon.Blood. 2001 May 1;97(9):2561-7. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.9.2561. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11313242
-
Increased CCAAT enhancer-binding protein epsilon (C/EBPepsilon) expression and premature apoptosis in myeloid cells expressing Gfi-1 N382S mutant associated with severe congenital neutropenia.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 21;281(16):10745-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510924200. Epub 2006 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16500901
-
Role of the Leucine Zipper Domain of CCAAT/ Enhancer Binding Protein-Epsilon (C/EBPε) in Neutrophil-Specific Granule Deficiency.Crit Rev Immunol. 2016;36(4):349-358. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2017019385. Crit Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28322138 Review.
-
Neutrophil specific granule deficiency and mutations in the gene encoding transcription factor C/EBP(epsilon).Curr Opin Hematol. 2002 Jan;9(1):36-42. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200201000-00007. Curr Opin Hematol. 2002. PMID: 11753076 Review.
Cited by
-
Hematopoietic transcription factor GFI1 promotes anchorage independence by sustaining ERK activity in cancer cells.J Clin Invest. 2022 Sep 1;132(17):e149551. doi: 10.1172/JCI149551. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35819844 Free PMC article.
-
Gfi-1 regulates the erythroid transcription factor network through Id2 repression in murine hematopoietic progenitor cells.Blood. 2014 Sep 4;124(10):1586-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-02-556522. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25051963 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital Neutropenia with Specific Granulocyte Deficiency Caused by Novel Double Heterozygous SMARCD2 Mutations.Hematol Rep. 2022 Sep 9;14(3):270-275. doi: 10.3390/hematolrep14030038. Hematol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36135322 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-23a~27a~24-2 microRNA cluster buffers transcription and signaling pathways during hematopoiesis.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jul 13;13(7):e1006887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006887. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28704388 Free PMC article.
-
Gfi-1 inhibits the expression of eosinophil major basic protein (MBP) during G-CSF-induced neutrophilic differentiation.Int J Hematol. 2012 Jun;95(6):640-7. doi: 10.1007/s12185-012-1078-x. Epub 2012 May 3. Int J Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22552881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellantuono I. Haemopoietic stem cells. Intl J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:607–620. - PubMed
-
- Berliner N. Molecular biology of neutrophil differentiation. Curr Opin Hematol. 1998;5:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Borregaard N, Theilgaard-Monch K, Sorensen O, Cowland J. Regulation of human neutrophil granule protein expression. Curr Opin Hematol. 2001;8:23–27. - PubMed
-
- Borregaard N, Sehested M, Nielsen BS, Sengelov H, Kjeldsen L. Biosynthesis of granule proteins in normal human bone marrow cells: gelatinase is a marker of terminal neutrophil differentiation. Blood. 1995;85:812–817. - PubMed
-
- Rosmarin A, Yang Z, Resendes K. Transcriptional regulation in myelopoiesis: hematopoietic fate choice, myeloid differentiation, and leukemogenesis. Expt Hematol. 2005;33:131–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

