Aspergillus nidulans Dis1/XMAP215 protein AlpA localizes to spindle pole bodies and microtubule plus ends and contributes to growth directionality
- PMID: 17237365
- PMCID: PMC1828926
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00266-06
Aspergillus nidulans Dis1/XMAP215 protein AlpA localizes to spindle pole bodies and microtubule plus ends and contributes to growth directionality
Abstract
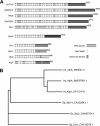
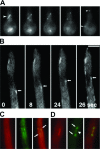
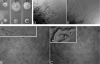
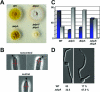
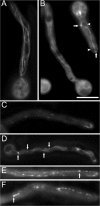
The dynamics of cytoplasmic microtubules (MTs) is largely controlled by a protein complex at the MT plus end. In Schizosaccharomyces pombe and in filamentous fungi, MT plus end-associated proteins also determine growth directionality. We have characterized the Dis1/XMAP215 family protein AlpA from Aspergillus nidulans and show that it determines MT dynamics as well as hyphal morphology. Green fluorescent protein-tagged AlpA localized to MT-organizing centers (centrosomes) and to MT plus ends. The latter accumulation occurred independently of conventional kinesin or the Kip2-familiy kinesin KipA. alpA deletion strains were viable and only slightly temperature sensitive. Mitosis, nuclear migration, and nuclear positioning were not affected, but hyphae grew in curves rather than straight, which appeared to be an effect of reduced MT growth and dynamics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cell-end marker TeaA and the microtubule polymerase AlpA contribute to microtubule guidance at the hyphal tip cortex of Aspergillus nidulans to provide polarity maintenance.J Cell Sci. 2013 Dec 1;126(Pt 23):5400-11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.129841. Epub 2013 Oct 7. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 24101725
-
The role of the kinesin motor KipA in microtubule organization and polarized growth of Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):497-506. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-02-0083. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15563609 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule plus end-tracking proteins play critical roles in directional growth of hyphae by regulating the dynamics of cytoplasmic microtubules in Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Nov;94(3):506-21. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12792. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25213466
-
Microtubule nucleation and organization without centrosomes.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018 Dec;46:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29981930 Review.
-
Interdependence of the actin and the microtubule cytoskeleton during fungal growth.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Aug;20:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 May 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24879477 Review.
Cited by
-
GTP is required for the microtubule catastrophe-inducing activity of MAP200, a tobacco homolog of XMAP215.Plant Physiol. 2009 Dec;151(4):1823-30. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.144303. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19854856 Free PMC article.
-
The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Nov;22(22):4343-61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0520. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21965297 Free PMC article.
-
Superresolution microscopy reveals a dynamic picture of cell polarity maintenance during directional growth.Sci Adv. 2015 Nov 13;1(10):e1500947. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500947. eCollection 2015 Nov. Sci Adv. 2015. PMID: 26665168 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mutants of the spindle pole body cause distinct alteration of cytoplasmic microtubules and nuclear dynamics in multinucleated hyphae.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 1;21(5):753-66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0555. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20053682 Free PMC article.
-
The Aspergillus nidulans kinesin-3 UncA motor moves vesicles along a subpopulation of microtubules.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(2):673-84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-07-0685. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19037104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Felenbok, B., M. Flipphi, and I. Nikolaev. 2001. Ethanol catabolism in Aspergillus nidulans: a model system for studying gene regulation. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 69:149-204. - PubMed
-
- Galagan, J. E., S. E. Calvo, C. Cuomo, L.-J. Ma, J. R. Wortman, S. Batzoglou, S.-I. Lee, M. Bastürkmen, C. C. Spevak, J. Clutterbuck, V. Kapitonov, J. Jurka, C. Scazzocchio, M. Farman, J. Butler, S. Purcell, S. Harris, G. H. Braus, O. Draht, S. Busch, C. d'Enfert, C. Bouchier, G. H. Goldman, D. Bell-Pedersen, S. Griffiths-Jones, J. H. Doonan, J. Yu, K. Vienken, A. Pain, M. Freitag, E. U. Selker, D. B. Archer, M. A. Peñalva, B. R. Oakley, M. Momany, T. Tanaka, T. Kumagai, K. Asai, M. Machida, W. C. Nierman, D. W. Denning, M. Caddick, M. Hynes, M. Paoletti, R. Fischer, B. Miller, P. Dyer, M. S. Sachs, S. A. Osmani, and B. W. Birren. 2005. Sequencing of Aspergillus nidulans and comparative analysis with A. fumigatus and A. oryzae. Nature 438:1105-1115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

