Nur77 converts phenotype of Bcl-B, an antiapoptotic protein expressed in plasma cells and myeloma
- PMID: 17227826
- PMCID: PMC1874560
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-11-056879
Nur77 converts phenotype of Bcl-B, an antiapoptotic protein expressed in plasma cells and myeloma
Erratum in
- Blood. 2009 Feb 12;113(7):1613
Abstract
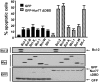
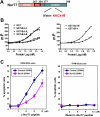
Defects in apoptosis mechanisms play important roles in malignancy and autoimmunity. Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77/TR3 has been demonstrated to bind antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and convert it from a cytoprotective to a cytodestructive protein, representing a phenotypic conversion mechanism. Of the 6 antiapoptotic human Bcl-2 family members, we found that Nur77/TR3 binds strongest to Bcl-B, showing selective reactivity with Bcl-B, Bcl-2, and Bfl-1 but not Bcl-X(L), Mcl-1, or Bcl-W. Nur77 converts the phenotype of Bcl-B from antiapoptotic to proapoptotic. Bcl-B is prominently expressed in plasma cells and multiple myeloma. Endogenous Bcl-B associates with endogenous Nur77 in RPMI 8226 myeloma cells, where RNA interference experiments demonstrated dependence on Bcl-B for Nur77-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, a Nur77-mimicking peptide killed RPMI 8226 myeloma cells through a Bcl-B-dependent mechanism. Because Bcl-B is abundantly expressed in plasma cells and some myelomas, these findings raise the possibility of exploiting the Nur77/Bcl-B mechanism for apoptosis for eradication of autoimmune plasma cells or myeloma.
Figures

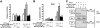

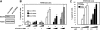
Similar articles
-
B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) residues essential for Bcl-2's apoptosis-inducing interaction with Nur77/Nor-1 orphan steroid receptors.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 30;293(13):4724-4734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001101. Epub 2018 Feb 2. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29414782 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3.Cell. 2004 Feb 20;116(4):527-40. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00162-x. Cell. 2004. PMID: 14980220
-
Targeting Nur77 translocation.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007 Jan;11(1):69-79. doi: 10.1517/14728222.11.1.69. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007. PMID: 17150035 Review.
-
A TR3/Nur77 peptide-based high-throughput fluorescence polarization screen for small molecule Bcl-B inhibitors.J Biomol Screen. 2008 Aug;13(7):665-73. doi: 10.1177/1087057108320918. Epub 2008 Jul 14. J Biomol Screen. 2008. PMID: 18626112
-
Nur77 family of nuclear hormone receptors.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004 Dec;3(4):413-23. doi: 10.2174/1568010042634523. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15584889 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct transcriptomes and autocrine cytokines underpin maturation and survival of antibody-secreting cells in systemic lupus erythematosus.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 1;15(1):1899. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46053-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38429276 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-2-family proteins and hematologic malignancies: history and future prospects.Blood. 2008 Apr 1;111(7):3322-30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-078162. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18362212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recruitment of plasma cells from IL-21-dependent and IL-21-independent immune reactions to the bone marrow.Nat Commun. 2024 May 17;15(1):4182. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48570-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38755157 Free PMC article.
-
Dichotomous roles for the orphan nuclear receptor NURR1 in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2013 Mar 21;13:139. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-139. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23517088 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C regulates mitochondrial targeting of Nur77 and its family member Nor-1 in thymocytes undergoing apoptosis.Eur J Immunol. 2010 Jul;40(7):2041-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.200940231. Eur J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20411565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green DR, Evan G. A matter of life and death. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:19–30. - PubMed
-
- O'Reilly LA, Strasser A. Apoptosis and autoimmune disease. Inflamm Res. 1999;48:5–21. - PubMed
-
- Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Lin B, Kolluri SK, Lin F, et al. Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor TR3/NGFI-B/Nur77. Cell. 2004;116:527–540. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Kolluri SK, Gu J, et al. Cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by mitochondrial targeting of nuclear orphan receptor TR3. Science. 2000;289:1159–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

