Intramolecular interaction in the tail of Acanthamoeba myosin IC between the SH3 domain and a putative pleckstrin homology domain
- PMID: 17215368
- PMCID: PMC1783391
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610231104
Intramolecular interaction in the tail of Acanthamoeba myosin IC between the SH3 domain and a putative pleckstrin homology domain
Abstract
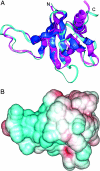
The 466-aa tail of the heavy chain of Acanthamoeba myosin IC (AMIC) comprises an N-terminal 220-residue basic region (BR) followed by a 56-residue Gly/Pro/Ala-rich region (GPA1), a 55-residue Src homology 3 (SH3) domain, and a C-terminal 135-residue Gly/Pro/Ala-rich region (GPA2). Cryo-electron microscopy of AMIC had shown previously that the AMIC tail is folded back on itself, suggesting the possibility of interactions between its N- and C-terminal regions. We now show specific differences between the NMR spectrum of bacterially expressed full-length tail and the sum of the spectra of individually expressed BR and GPA1-SH3-GPA2 (GSG) regions. These results are indicative of interactions between the two subdomains in the full-length tail. From the NMR data, we could assign many of the residues in BR and GSG that are involved in these interactions. By combining homology modeling with the NMR data, we identify a putative pleckstrin homology (PH) domain within BR, and show that the PH domain interacts with the SH3 domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Acanthamoeba myosin IC colocalizes with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate at the plasma membrane due to the high concentration of negative charge.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 14;283(46):32014-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804828200. Epub 2008 Sep 4. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18772133 Free PMC article.
-
Subdomain organization of the Acanthamoeba myosin IC tail from cryo-electron microscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Aug 17;101(33):12189-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404835101. Epub 2004 Aug 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15302934 Free PMC article.
-
Organization and ligand binding properties of the tail of Acanthamoeba myosin-IA. Identification of an actin-binding site in the basic (tail homology-1) domain.J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 3;274(49):35159-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.49.35159. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10574999
-
Acan125 binding to the SH3 domain of acanthamoeba myosin-IC.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Mar 1;375(1):161-4. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1648. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10683262
-
Functional analysis of tail domains of Acanthamoeba myosin IC by characterization of truncation and deletion mutants.J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 11;275(32):24886-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004287200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10840041
Cited by
-
Allosteric properties of PH domains in Arf regulatory proteins.Cell Logist. 2016 Apr 26;6(2):e1181700. doi: 10.1080/21592799.2016.1181700. eCollection 2016 Apr-Jun. Cell Logist. 2016. PMID: 27294009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myosin 1G is an abundant class I myosin in lymphocytes whose localization at the plasma membrane depends on its ancient divergent pleckstrin homology (PH) domain (Myo1PH).J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 19;285(12):8675-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.086959. Epub 2010 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20071333 Free PMC article.
-
Acanthamoeba myosin IC colocalizes with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate at the plasma membrane due to the high concentration of negative charge.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 14;283(46):32014-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804828200. Epub 2008 Sep 4. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18772133 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of dynamic relocalization of Dictyostelium myosin IB.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14923-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.318667. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22367211 Free PMC article.
-
The S. pombe adaptor protein Bbc1 regulates localization of Wsp1 and Vrp1 during endocytic actin patch assembly.J Cell Sci. 2019 Sep 11;132(17):jcs233502. doi: 10.1242/jcs.233502. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31391237 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

