Identification and characterization of peptides that interact with hepatitis B virus via the putative receptor binding site
- PMID: 17192308
- PMCID: PMC1866126
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01270-06
Identification and characterization of peptides that interact with hepatitis B virus via the putative receptor binding site
Abstract
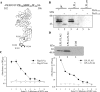
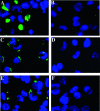
A direct involvement of the PreS domain of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) large envelope protein, and in particular amino acid residues 21 to 47, in virus attachment to hepatocytes has been suggested by many previous studies. Several PreS-interacting proteins have been identified. However, they share few common sequence motifs, and a bona fide cellular receptor for HBV remains elusive. In this study, we aimed to identify PreS-interacting motifs and to search for novel HBV-interacting proteins and the long-sought receptor. PreS fusion proteins were used as baits to screen a phage display library of random peptides. A group of PreS-binding peptides were obtained. These peptides could bind to amino acids 21 to 47 of PreS1 and shared a linear motif (W1T2X3W4W5) sufficient for binding specifically to PreS and viral particles. Several human proteins with such a motif were identified through BLAST search. Analysis of their biochemical and structural properties suggested that lipoprotein lipase (LPL), a key enzyme in lipoprotein metabolism, might interact with PreS and HBV particles. The interaction of HBV with LPL was demonstrated by in vitro binding, virus capture, and cell attachment assays. These findings suggest that LPL may play a role in the initiation of HBV infection. Identification of peptides and protein ligands corresponding to LPL that bind to the HBV envelope will offer new therapeutic strategies against HBV infection.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Asialoglycoprotein receptor interacts with the preS1 domain of hepatitis B virus in vivo and in vitro.Arch Virol. 2011 Apr;156(4):637-45. doi: 10.1007/s00705-010-0903-x. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Arch Virol. 2011. PMID: 21207081
-
Detection of cellular receptors specific for the hepatitis B virus preS surface protein on cell lines of extrahepatic origin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Oct 14;277(1):246-54. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3661. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 11027670
-
Characterization of a hepatitis B and hepatitis delta virus receptor binding site.Hepatology. 2006 Apr;43(4):750-60. doi: 10.1002/hep.21112. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16557545
-
Applications of human hepatitis B virus preS domain in bio- and nanotechnology.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7400-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7400. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attachment sites and neutralising epitopes of hepatitis B virus.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2006 Mar;52(1):3-21. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2006. PMID: 16554703 Review.
Cited by
-
Infectivity determinants of the hepatitis B virus pre-S domain are confined to the N-terminal 75 amino acid residues.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5841-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00096-07. Epub 2007 Mar 21. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17376925 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the mystery of hepatitis B virus receptors: A historical perspective.Virusdisease. 2015 Sep;26(3):97-104. doi: 10.1007/s13337-015-0260-1. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Virusdisease. 2015. PMID: 26396975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Antivirals Using Phage Display.Viruses. 2021 Jun 10;13(6):1120. doi: 10.3390/v13061120. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34200959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen interacts with and promotes cyclophilin a secretion: possible link to pathogenesis of HBV infection.J Virol. 2010 Apr;84(7):3373-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02555-09. Epub 2010 Jan 20. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20089655 Free PMC article.
-
Development of peptides targeting receptor binding site of the envelope glycoprotein to contain the West Nile virus infection.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 11;11(1):20131. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99696-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34635758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auwerx, J. H., S. Deeb, J. D. Brunzell, G. Wolfbauer, and A. Chait. 1989. Lipoprotein lipase gene expression in THP-1 cells. Biochemistry. 28:4563-4567. - PubMed
-
- Bartosch B., and F. L. Cosset. 2006. Cell entry of hepatitis C virus. Virology 348:1-12. - PubMed
-
- Burritt, J. B., C. W. Bond, K. W. Doss, and A. J. Jesaitis. 1996. Filamentous phage display of oligopeptide libraries. Anal. Biochem. 238:1-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

