Gefitinib (IRESSA) sensitive lung cancer cell lines show phosphorylation of Akt without ligand stimulation
- PMID: 17150102
- PMCID: PMC1698934
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-277
Gefitinib (IRESSA) sensitive lung cancer cell lines show phosphorylation of Akt without ligand stimulation
Abstract
Background: Phase III trials evaluating the efficacy of gefitinib (IRESSA) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) lend support to the need for improved patient selection in terms of gefitinib use. Mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene is reported to be associated with clinical responsiveness to gefitinib. However, gefitinib-sensitive and prolonged stable-disease-defined tumors without EGFR gene mutation have also been reported.
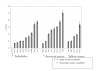
Methods: To identify other key factors involved in gefitinib sensitivity, we analyzed the protein expression of molecules within the EGFR family, PI3K-Akt and Ras/MEK/Erk pathways and examined the sensitivity to gefitinib using the MTT cell proliferation assay in 23 lung cancer cell lines.
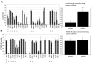
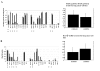
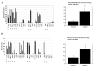
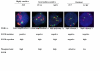
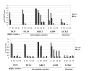
Results: We identified one highly sensitive cell line (PC9), eight cell lines displaying intermediate-sensitivity, and 14 resistant cell lines. Only PC9 and PC14 (intermediate-sensitivity) displayed an EGFR gene mutation including amplification. Eight out of the nine cell lines showing sensitivity had Akt phosphorylation without ligand stimulation, while only three out of the 14 resistant lines displayed this characteristic (P = 0.0059). Furthermore, the ratio of phosphor-Akt/total Akt in sensitive cells was higher than that observed in resistant cells (P = 0.0016). Akt phosphorylation was partially inhibited by gefitinib in all sensitive cell lines.
Conclusion: These results suggest that Akt phosphorylation without ligand stimulation may play a key signaling role in gefitinib sensitivity, especially intermediate-sensitivity. In addition, expression analyses of the EGFR family, EGFR gene mutation, and FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) analyses showed that the phosphorylated state of EGFR and Akt might be a useful clinical marker of Akt activation without ligand stimulation, in addition to EGFR gene mutation and amplification, particularly in adenocarcinomas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimization of patient selection for gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer by combined analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation, K-ras mutation, and Akt phosphorylation.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 15;12(8):2538-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2845. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16638863
-
Blocking the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling pathways can overcome gefitinib-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Adv Med Sci. 2011;56(2):275-84. doi: 10.2478/v10039-011-0043-x. Adv Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22037177
-
Reduction of PTEN protein and loss of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in lung cancer with natural resistance to gefitinib (IRESSA).Br J Cancer. 2005 May 9;92(9):1711-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602559. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15870831 Free PMC article.
-
An update of the mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: Gefitinib (Iressa) -induced changes in the expression and nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of HER-ligands (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2007 Jul;20(1):3-10. Int J Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17549382 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006 Jan;1(1):1-13. doi: 10.2174/157488706775246157. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006. PMID: 18393776 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of network branching in eliciting differential short-term signaling responses in the hypersensitive epidermal growth factor receptor mutants implicated in lung cancer.Biotechnol Prog. 2008 May-Jun;24(3):540-53. doi: 10.1021/bp070405o. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Biotechnol Prog. 2008. PMID: 18412405 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinase USP9X regulates RIT1 protein abundance and oncogenic phenotypes.iScience. 2024 Jul 14;27(8):110499. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110499. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39161959 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming resistance of targeted EGFR monotherapy by inhibition of STAT3 escape pathway in soft tissue sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):21496-509. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7452. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26909593 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells to 5-FU/S-1 via down-regulation of thymidylate synthase expression and up-regulation of p21(waf1/cip1) expression.Cancer Sci. 2010 Jun;101(6):1424-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01559.x. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20384633 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is transcriptionally induced by the Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) and can be inhibited with Iressa in basal-like breast cancer, providing a potential target for therapy.Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(5):R61. doi: 10.1186/bcr1767. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rusch V, Baselga J, Cordon-Cardo C, Orazem J, Zaman M, Hoda S, McIntosh J, Dmitrovsky E. Differential expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in primary non-small cell lung cancers and adjacent benign lung. Cancer Res. 1993;53:2379–85. - PubMed
-
- Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;19:183–232. - PubMed
-
- Ferry D, Hammond L, Ranson M, Kris MG, Miller V, Murray P, Tullo a, Feyereislova A, Rowinsky E. Intermittent oral ZD1839 (Iressa), a novel epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI), shows evidence of good tolerability and activity: final results from a Phase I study. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2000;19:3a. (abstract 5E)
-
- Ranson M, Hammond LA, Ferry D, Kris M, Tullo A, Murray PI, Averbuch S, Ochs J, Morris C, Feyereislova a, Swaisland H, Rowinsky EK. ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is well tolerated and active in patients with solid, malignant tumors: results of a phase I trial. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2240–2250. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.10.112. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Pemberton K, Archer V. Results of a Phase III placebo-controlled study (ISEL) of gefitinib (IRESSA) plus best supportive care (BSC) in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who had received 1 or 2 prior chemotherapy regimens. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2005;46 (abstract. LB-6)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

