Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited
- PMID: 17149751
- PMCID: PMC1878509
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.21139
Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited
Abstract
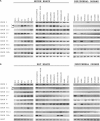
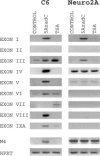
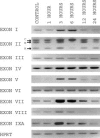
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has important functions in the development of the nervous system and in brain plasticity-related processes such as memory, learning, and drug addiction. Despite the fact that the function and regulation of rodent BDNF gene expression have received close attention during the last decade, knowledge of the structural organization of mouse and rat BDNF gene has remained incomplete. We have identified and characterized several mouse and rat BDNF transcripts containing novel 5' untranslated exons and introduced a new numbering system for mouse and rat BDNF exons. According to our results both mouse and rat BDNF gene consist of eight 5' untranslated exons and one protein coding 3' exon. Transcription of the gene results in BDNF transcripts containing one of the eight 5' exons spliced to the protein coding exon and in a transcript containing only 5' extended protein coding exon. We also report the distinct tissue-specific expression profiles of each of the mouse and rat 5' exon-specific transcripts in different brain regions and nonneural tissues. In addition, we show that kainic acid-induced seizures that lead to changes in cellular Ca(2+) levels as well as inhibition of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation contribute to the differential regulation of the expression of BDNF transcripts. Finally, we confirm that mouse and rat BDNF gene loci do not encode antisense mRNA transcripts, suggesting that mechanisms of regulation for rodent and human BDNF genes differ substantially.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rodent BDNF genes, novel promoters, novel splice variants, and regulation by cocaine.Brain Res. 2006 Jan 5;1067(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.10.004. Epub 2005 Dec 22. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16376315
-
Expression changes of multiple brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts in selective spinal nerve ligation model and complete Freund's adjuvant model.Brain Res. 2008 Apr 24;1206:13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.12.004. Epub 2007 Dec 8. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18353280
-
Differential regulation of multiple brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts in the postnatal and adult rat hippocampus during development, and in response to kainate administration.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Nov 4;130(1-2):170-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.08.002. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15519687
-
Regulation of BDNF expression by cocaine.Yale J Biol Med. 2012 Dec;85(4):437-46. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Yale J Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 23239946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in physiological and pathological conditions.Clin Sci (Lond). 2017 Jan 1;131(2):123-138. doi: 10.1042/CS20160009. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28011898 Review.
Cited by
-
An HDAC-dependent epigenetic mechanism that enhances the efficacy of the antidepressant drug fluoxetine.Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 2;5:8171. doi: 10.1038/srep08171. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25639887 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd45b and N-methyl-D-aspartate induced DNA demethylation in postmitotic neurons.Epigenomics. 2015;7(4):567-79. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.12. Epigenomics. 2015. PMID: 26111030 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Response and Perinatal Reprogramming: Unraveling (Mal)adaptive Strategies.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:6752193. doi: 10.1155/2016/6752193. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27057367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative analysis of BDNF/TrkB protein and mRNA in cortical and striatal neurons using α-tubulin as a normalization factor.Cytometry A. 2012 Aug;81(8):704-17. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22073. Epub 2012 May 30. Cytometry A. 2012. PMID: 22649026 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Modifications in Stress Response Genes Associated With Childhood Trauma.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Nov 8;10:808. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00808. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31780969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ballas N, Mandel G. The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neuronal genes. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15:500–506. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–657. - PubMed
-
- Baranova A, Hammarsund M, Ivanov D, Skoblov M, Sangfelt O, Corcoran M, Borodina T, Makeeva N, Pestova A, Tyazhelova T, et al. Distinct organization of the candidate tumor suppressor gene RFP2 in human and mouse: multiple mRNA isoforms in both species- and human-specific antisense transcript RFP2OS. Gene. 2003;321:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Bibel M, Barde YA. Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2919–2937. - PubMed
-
- Binder DK. The role of BDNF in epilepsy and other diseases of the mature nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004;548:34–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

