Mitotic kinesin-like protein 2 binds and colocalizes with papillomavirus E2 during mitosis
- PMID: 17135315
- PMCID: PMC1797594
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01638-06
Mitotic kinesin-like protein 2 binds and colocalizes with papillomavirus E2 during mitosis
Abstract
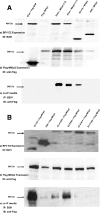
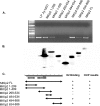
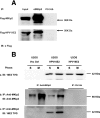
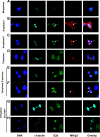
MKlp2 is a kinesin-like motor protein of the central mitotic spindle required for completion of cytokinesis. Papillomavirus E2 is a sequence specific DNA binding protein that regulates viral transcription and replication and is responsible for partitioning viral episomes into daughter cells during cell division. We demonstrate that MKlp2 specifically associates with the E2 protein during mitosis. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we show viral genomes are in complex with MKlp2 only within this stage of cell cycle. By immunofluorescence, a subpopulation of papillomavirus E2 colocalizes with MKlp2 in the midbody/midplate during late mitosis. We conclude that during specific stages of mitosis, the papillomavirus E2 protein binds to MKlp2, and infer that association with this motor protein ensures viral genome partitioning during cytokinesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The papillomavirus E2 proteins.Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):57-79. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23849793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cellular DNA Helicase ChlR1 Regulates Chromatin and Nuclear Matrix Attachment of the Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 Protein and High-Copy-Number Viral Genome Establishment.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01853-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01853-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795438 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with TopBP1 Is Required for Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 Plasmid Segregation/Retention Function during Mitosis.J Virol. 2022 Aug 24;96(16):e0083022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00830-22. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35880889 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic localization of the human papillomavirus type 11 origin binding protein E2 through mitosis while in association with the spindle apparatus.J Virol. 2006 May;80(10):4792-800. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.4792-4800.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16641272 Free PMC article.
-
Partitioning viral genomes in mitosis: same idea, different targets.Cell Cycle. 2006 Jul;5(14):1499-502. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.14.3094. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16861919 Review.
Cited by
-
Current understanding of the role of the Brd4 protein in the papillomavirus lifecycle.Viruses. 2013 May 30;5(6):1374-94. doi: 10.3390/v5061374. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23722886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The papillomavirus E2 proteins.Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):57-79. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23849793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of HPV-16 E2 at serine 243 enables binding to Brd4 and mitotic chromosomes.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 23;9(10):e110882. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110882. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25340539 Free PMC article.
-
The selfish yeast plasmid uses the nuclear motor Kip1p but not Cin8p for its localization and equal segregation.J Cell Biol. 2009 Apr 20;185(2):251-64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810130. Epub 2009 Apr 13. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19364922 Free PMC article.
-
The HPV E2-Host Protein-Protein Interactions: A Complex Hijacking of the Cellular Network.Open Virol J. 2012;6:173-89. doi: 10.2174/1874357901206010173. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Open Virol J. 2012. PMID: 23341853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastien, N., and A. A. McBride. 2000. Interaction of the papillomavirus E2 protein with mitotic chromosomes. Virology 270:124-134. - PubMed
-
- Bellanger, S., S. Blachon, F. Mechali, C. Bonne-Andrea, and F. Thierry. 2005. High-risk but not low-risk HPV E2 proteins bind to the APC activators Cdh1 and Cdc20 and cause genomic instability. Cell Cycle 4:1608-1615. - PubMed
-
- Breiding, D. E., M. J. Grossel, and E. J. Androphy. 1996. Genetic analysis of the bovine papillomavirus E2 transcriptional activation domain. Virology 221:34-43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

