Sodium-coupled glucose cotransporters contribute to hypothalamic glucose sensing
- PMID: 17130483
- PMCID: PMC1948974
- DOI: 10.2337/db06-0531
Sodium-coupled glucose cotransporters contribute to hypothalamic glucose sensing
Abstract
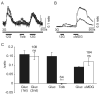
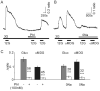
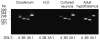
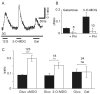
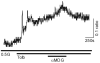
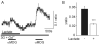
Specialized neurons within the hypothalamus have the ability to sense and respond to changes in ambient glucose concentrations. We investigated the mechanisms underlying glucose-triggered activity in glucose-excited neurons, using primary cultures of rat hypothalamic neurons monitored by fluorescence calcium imaging. We found that 35% (738 of 2,139) of the neurons were excited by increasing glucose from 3 to 15 mmol/l, but only 9% (6 of 64) of these glucose-excited neurons were activated by tolbutamide, suggesting the involvement of a ATP-sensitive K(+) channel-independent mechanism. alpha-Methylglucopyranoside (alphaMDG; 12 mmol/l), a nonmetabolizable substrate of sodium glucose cotransporters (SGLTs), mimicked the effect of high glucose in 67% of glucose-excited neurons, and both glucose- and alphaMDG-triggered excitation were blocked by Na(+) removal or by the SGLT inhibitor phloridzin (100 nmol/l). In the presence of 0.5 mmol/l glucose and tolbutamide, responses could also be triggered by 3.5 mmol/l alphaMDG, supporting a role for an SGLT-associated mechanism at low as well as high substrate concentrations. Using RT-PCR, we detected SGLT1, SGLT3a, and SGLT3b in both cultured neurons and adult rat hypothalamus. Our findings suggest a novel role for SGLTs in glucose sensing by hypothalamic glucose-excited neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dissociation between sensing and metabolism of glucose in sugar sensing neurones.J Physiol. 2009 Jan 15;587(1):41-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.163410. Epub 2008 Nov 3. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18981030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of glucose-excited neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus by glucose and feeding-relevant peptides.Diabetes. 2004 Aug;53(8):1959-65. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.8.1959. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 15277373
-
Differential effects of glucose and lactate on glucosensing neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus.Diabetes. 2005 Jan;54(1):15-22. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.1.15. Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 15616006
-
Glucokinase is a critical regulator of ventromedial hypothalamic neuronal glucosensing.Diabetes. 2006 Feb;55(2):412-20. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-1229. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16443775
-
Biology of human sodium glucose transporters.Physiol Rev. 2011 Apr;91(2):733-94. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00055.2009. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21527736 Review.
Cited by
-
Does nutrient sensing determine how we "see" food?Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Jun;15(6):604. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0604-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 25956822 Review.
-
Repurposing SGLT2 Inhibitors for Neurological Disorders: A Focus on the Autism Spectrum Disorder.Molecules. 2022 Oct 23;27(21):7174. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217174. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT6 - A pharmacological target for the treatment of obesity?Adipocyte. 2018;7(4):277-284. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2018.1516098. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Adipocyte. 2018. PMID: 30161013 Free PMC article.
-
Brain glucose sensing, glucokinase and neural control of metabolism and islet function.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Sep;16 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):26-32. doi: 10.1111/dom.12334. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 25200293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Genetic Screen Identifies Hypothalamic Fgf15 as a Regulator of Glucagon Secretion.Cell Rep. 2016 Nov 8;17(7):1795-1806. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.041. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27829151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oomura Y, Ono T, Ooyama H, Wayner MJ. Glucose and osmosensitive neurons of the rat hypothalamus. Nature. 1969;222:282–284. - PubMed
-
- Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA, Routh VH. Brain glucose sensing and body energy homeostasis: role in obesity and diabetes. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:R1223–1231. - PubMed
-
- Ashford ML, Boden PR, Treherne JM. Glucose-induced excitation of hypothalamic neurons is mediated by ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Pflugers Arch. 1990;415:479–483. - PubMed
-
- Routh VH, McArdle JJ, Levin BE. Phosphorylation modulates the activity of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus. Brain Res. 1997;778:107–119. - PubMed
-
- Jetton TL, Liang Y, Pettepher CC, Zimmerman EC, Cox FG, Horvath K, Matschinsky FM, Magnuson MA. Analysis of upstream glucokinase promoter activity in transgenic mice and identification of glucokinase in rare neuroendocrine cells in the brain and gut. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:3641–3654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

