RNAi therapeutics: a potential new class of pharmaceutical drugs
- PMID: 17108989
- PMCID: PMC7097247
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio839
RNAi therapeutics: a potential new class of pharmaceutical drugs
Abstract
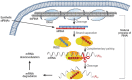
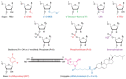
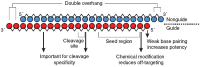
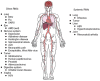
The rapid identification of highly specific and potent drug candidates continues to be a substantial challenge with traditional pharmaceutical approaches. Moreover, many targets have proven to be intractable to traditional small-molecule and protein approaches. Therapeutics based on RNA interference (RNAi) offer a powerful method for rapidly identifying specific and potent inhibitors of disease targets from all molecular classes. Numerous proof-of-concept studies in animal models of human disease demonstrate the broad potential application of RNAi therapeutics. The major challenge for successful drug development is identifying delivery strategies that can be translated to the clinic. With advances in this area and the commencement of multiple clinical trials with RNAi therapeutic candidates, a transformation in modern medicine may soon be realized.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employees of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Harnessing RNA interference to develop neonatal therapies: from Nobel Prize winning discovery to proof of concept clinical trials.Early Hum Dev. 2009 Oct;85(10 Suppl):S31-5. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2009.08.013. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Early Hum Dev. 2009. PMID: 19833462
-
RNA interference strategies as therapy for respiratory viral infections.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008 Oct;27(10 Suppl):S118-22. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318168b759. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008. PMID: 18820571
-
RNAi-based drug discovery and its application to therapeutics.IDrugs. 2008 Apr;11(4):274-8. IDrugs. 2008. PMID: 18379962
-
The promise, pitfalls and progress of RNA-interference-based antiviral therapy for respiratory viruses.Antivir Ther. 2012;17(1 Pt B):213-25. doi: 10.3851/IMP2064. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Antivir Ther. 2012. PMID: 22311654 Review.
-
siRNA and the lung: research tool or therapeutic drug?Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;8(3):280-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.04.005. Epub 2008 May 14. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18485820 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the HYDRAtion method for loading siRNA on liposomes: the interplay between stability and biological activity in human undiluted ascites fluid.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017 Apr;7(2):241-251. doi: 10.1007/s13346-016-0329-4. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 27631392
-
Intraluminal delivery of thrombospondin-2 small interfering RNA inhibits the vascular response to injury in a rat carotid balloon angioplasty model.FASEB J. 2017 Jan;31(1):109-119. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600501R. Epub 2016 Sep 26. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 27671229 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomal and lysosomal degradation for specific and durable suppression of immunotherapeutic targets.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 Aug 15;17(3):583-598. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0066. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32944392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of canonical versus Dicer-substrate siRNA in vitro and in vivo.RNA. 2012 Mar;18(3):557-68. doi: 10.1261/rna.031120.111. Epub 2012 Jan 31. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22294662 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Nucleosidic Analogues of Polyaminonucleosides and Their Influence on Thermodynamic Properties of Derived Oligonucleotides.Molecules. 2015 Jul 13;20(7):12652-69. doi: 10.3390/molecules200712652. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26184145 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

