A hypervariable region within the 3' cis-acting element of the murine coronavirus genome is nonessential for RNA synthesis but affects pathogenesis
- PMID: 17093194
- PMCID: PMC1797510
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00803-06
A hypervariable region within the 3' cis-acting element of the murine coronavirus genome is nonessential for RNA synthesis but affects pathogenesis
Abstract
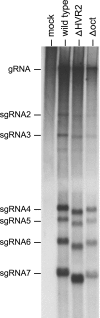
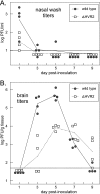
The 3' cis-acting element for mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) RNA synthesis resides entirely within the 301-nucleotide 3' untranslated region (3' UTR) of the viral genome and consists of three regions. Encompassing the upstream end of the 3' UTR are a bulged stem-loop and an overlapping RNA pseudoknot, both of which are essential to MHV and common to all group 2 coronaviruses. At the downstream end of the genome is the minimal signal for initiation of negative-strand RNA synthesis. Between these two ends is a hypervariable region (HVR) that is only poorly conserved between MHV and other group 2 coronaviruses. Paradoxically, buried within the HVR is an octanucleotide motif (oct), 5'-GGAAGAGC-3', which is almost universally conserved in coronaviruses and is therefore assumed to have a critical biological function. We conducted an extensive mutational analysis of the HVR. Surprisingly, this region tolerated numerous deletions, rearrangements, and point mutations. Most striking, a mutant deleted of the entire HVR was only minimally impaired in tissue culture relative to the wild type. By contrast, the HVR deletion mutant was highly attenuated in mice, causing no signs of clinical disease and minimal weight loss compared to wild-type virus. Correspondingly, replication of the HVR deletion mutant in the brains of mice was greatly reduced compared to that of the wild type. Our results show that neither the HVR nor oct is essential for the basic mechanism of MHV RNA synthesis in tissue culture. However, the HVR appears to play a significant role in viral pathogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of the RNA components of a putative molecular switch in the 3' untranslated region of the murine coronavirus genome.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(2):669-82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.2.669-682.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14694098 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of mutations in the mouse hepatitis virus 3'(+)42 protein binding element on RNA replication.J Virol. 2005 Dec;79(23):14570-85. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14570-14585.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16282457 Free PMC article.
-
An essential secondary structure in the 3' untranslated region of the mouse hepatitis virus genome.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;440:297-302. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5331-1_39. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 9782296
-
Genetic interactions between an essential 3' cis-acting RNA pseudoknot, replicase gene products, and the extreme 3' end of the mouse coronavirus genome.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(3):1214-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01690-07. Epub 2007 Nov 21. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18032506 Free PMC article.
-
The structure and functions of coronavirus genomic 3' and 5' ends.Virus Res. 2015 Aug 3;206:120-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.02.025. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25736566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2203:1-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0900-2_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32833200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoinformatics and Molecular Docking Studies Predicted Potential Multiepitope-Based Peptide Vaccine and Novel Compounds against Novel SARS-CoV-2 through Virtual Screening.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 26;2021:1596834. doi: 10.1155/2021/1596834. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33728324 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-RNA and RNA-protein interactions in coronavirus replication and transcription.RNA Biol. 2011 Mar-Apr;8(2):237-48. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.2.14991. Epub 2011 Mar 1. RNA Biol. 2011. PMID: 21378501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1282:1-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25720466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subgenomic messenger RNA amplification in coronaviruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 6;107(27):12257-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000378107. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20562343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boursnell, M. E. G., M. M. Binns, I. J. Foulds, and T. D. K. Brown. 1985. Sequences of the nucleocapsid genes from two strains of avian infectious bronchitis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 66:573-580. - PubMed
-
- Chua, M. M., K. C. MacNamara, L. San Mateo, H. Shen, and S. R. Weiss. 2004. Effects of an epitope-specific CD8+ T-cell response on murine coronavirus central nervous system disease: protection from virus replication and antigen spread and selection of epitope escape mutants. J. Virol. 78:1150-1159. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

