Arabidopsis GCN5, HD1, and TAF1/HAF2 interact to regulate histone acetylation required for light-responsive gene expression
- PMID: 17085686
- PMCID: PMC1693931
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.043489
Arabidopsis GCN5, HD1, and TAF1/HAF2 interact to regulate histone acetylation required for light-responsive gene expression
Abstract
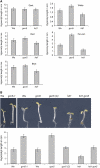
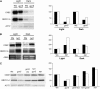
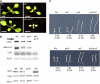
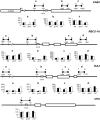
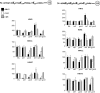
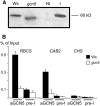
We previously showed that Arabidopsis thaliana histone acetyltransferase TAF1/HAF2 is required for the light regulation of growth and gene expression, and we show here that histone acetyltransferase GCN5 and histone deacetylase HD1/HDA19 are also involved in such regulation. Mutation of GCN5 resulted in a long-hypocotyl phenotype and reduced light-inducible gene expression, whereas mutation of HD1 induced opposite effects. The double mutant gcn5 hd1 restored a normal photomorphogenic phenotype. By contrast, the double mutant gcn5 taf1 resulted in further loss of light-regulated gene expression. gcn5 reduced acetylation of histones H3 and H4, mostly on the core promoter regions, whereas hd1 increased acetylation on both core and more upstream promoter regions. GCN5 and TAF1 were both required for H3K9, H3K27, and H4K12 acetylation on the target promoters, but H3K14 acetylation was dependent only on GCN5. Interestingly, gcn5 taf1 had a cumulative effect mainly on H3K9 acetylation. On the other hand, hd1 induced increased acetylation on H3K9, H3K27, H4K5, and H4K8. GCN5 was also shown to be directly associated with the light-responsive promoters. These results suggest that acetylation of specific histone Lys residues, regulated by GCN5, TAF1, and HD1, is required for light-regulated gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis HAF2 gene encoding TATA-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor TAF1, is required to integrate light signals to regulate gene expression and growth.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 14;280(2):1465-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409000200. Epub 2004 Nov 3. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15525647
-
Histone acetyltransferase GCN5 is essential for heat stress-responsive gene activation and thermotolerance in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2015 Dec;84(6):1178-91. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13076. Plant J. 2015. PMID: 26576681
-
Histone acetyltransferase GCN5 interferes with the miRNA pathway in Arabidopsis.Cell Res. 2009 Jul;19(7):899-909. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.59. Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19436261
-
Updated Mechanisms of GCN5-The Monkey King of the Plant Kingdom in Plant Development and Resistance to Abiotic Stresses.Cells. 2021 Apr 22;10(5):979. doi: 10.3390/cells10050979. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33922251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone acetyltransferase AtGCN5/HAG1 is a versatile regulator of developmental and inducible gene expression in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2010 Jul;3(4):670-7. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq018. Epub 2010 May 9. Mol Plant. 2010. PMID: 20457643 Review.
Cited by
-
HAG1 and SWI3A/B control of male germ line development in P. patens suggests conservation of epigenetic reproductive control across land plants.Plant Reprod. 2021 Jun;34(2):149-173. doi: 10.1007/s00497-021-00409-0. Epub 2021 Apr 11. Plant Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33839924 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine acetylation of histone acetyltransferase adaptor protein ADA2 is a mechanism of metabolic control of chromatin modification in plants.Nat Plants. 2024 Mar;10(3):439-452. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01623-0. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Nat Plants. 2024. PMID: 38326652
-
The Banana Transcriptional Repressor MaDEAR1 Negatively Regulates Cell Wall-Modifying Genes Involved in Fruit Ripening.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jul 11;7:1021. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01021. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27462342 Free PMC article.
-
Tobacco TTG2 regulates vegetative growth and seed production via the predominant role of ARF8 in cooperation with ARF17 and ARF19.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Jun 2;16(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0815-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27255279 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing SlELP2L, a tomato Elongator complex protein 2-like gene, inhibits leaf growth, accelerates leaf, sepal senescence, and produces dark-green fruit.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 9;5:7693. doi: 10.1038/srep07693. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25573793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayadi, M., Delaporte, V., Li, Y.F., and Zhou, D.X. (2004). Analysis of GT-3a identifies a distinct subgroup of trihelix DNA-binding transcription factors in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 562 147–154. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S.L. (2002). Histone modification in transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12 142–148. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand, C., Benhamed, M., Li, Y.F., Ayadi, M., Lemonnier, G., Renou, J.P., Delarue, M., and Zhou, D.X. (2005). Arabidopsis HAF2 gene encoding TATA-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor TAF1, is required to integrate light signals to regulate gene expression and growth. J. Biol. Chem. 280 1465–1473. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand, C., Bergounioux, C., Domenichini, S., Delarue, M., and Zhou, D.X. (2003). Arabidopsis histone acetyltransferase GCN5 regulates the floral meristem activity through the WUSCHEL/AGAMOUS pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 278 28246–28251. - PubMed
-
- Carrozza, M.J., Utley, R.T., Workman, J.L., and Côté, J. (2003). The diverse function of histone acetyltransferase complexes. Trends Genet. 19 321–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

