Template disruptions and failure of double Holliday junction dissolution during double-strand break repair in Drosophila BLM mutants
- PMID: 17075047
- PMCID: PMC1636541
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607904103
Template disruptions and failure of double Holliday junction dissolution during double-strand break repair in Drosophila BLM mutants
Abstract
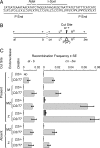
Previous biochemical studies of the BLM gene product have shown its ability in conjunction with topoisomerase IIIalpha to resolve double Holliday structures through a process called "dissolution." This process could prevent crossing over during repair of double-strand breaks. We report an analysis of the Drosophila BLM gene, DmBlm, in the repair of double-strand breaks in the premeiotic germ line of Drosophila males. With a repair reporter construct, Rr3, and other genetic tools, we show that DmBlm mutants are defective for homologous repair but show a compensating increase in single-strand annealing. Increases of 40- to 50-fold in crossing over and flanking deletions also were seen. Perhaps most significantly, the template used for homologous repair in DmBlm mutants is itself subject to deletions and complex rearrangements. These template disruptions are indicative of failure to resolve double Holliday junctions. These findings, along with the demonstration that a weak allele of topoisomerase IIIalpha has some of the same defects as DmBlm, support the dissolution model. Finally, an analysis of DmBlm mutants in conjunction with mus81 or spnA (Rad51) reveals a second function of BLM distinct from the repair of induced double-strand breaks and possibly related to maintenance of replication forks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
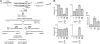



Similar articles
-
In vivo analysis of Drosophila BLM helicase function during DNA double-strand gap repair.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;587:185-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-355-8_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20225150
-
Formation of deletions during double-strand break repair in Drosophila DmBlm mutants occurs after strand invasion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 2;101(44):15694-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406157101. Epub 2004 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15501916 Free PMC article.
-
Three structure-selective endonucleases are essential in the absence of BLM helicase in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002315. Epub 2011 Oct 13. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22022278 Free PMC article.
-
Investigations of homologous recombination pathways and their regulation.Yale J Biol Med. 2013 Dec 13;86(4):453-61. Yale J Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24348209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Holliday junction processing enzymes as guardians of genome stability.Trends Biochem Sci. 2014 Sep;39(9):409-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014. PMID: 25131815 Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila bloom helicase maintains genome integrity by inhibiting recombination between divergent DNA sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Dec;36(21):6907-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn793. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18978019 Free PMC article.
-
Two closely related RecQ helicases have antagonistic roles in homologous recombination and DNA repair in Arabidopsis thaliana.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Nov 20;104(47):18836-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705998104. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18000056 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the mus309 mutation, defective in DNA double-strand break repair, on crossing over in Drosophila melanogaster suggests a mechanism for the centromere effect of crossing over.Genetica. 2010 Mar;138(3):333-42. doi: 10.1007/s10709-009-9422-7. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Genetica. 2010. Retraction in: Genetica. 2010 Dec;138(11-12):1307. doi: 10.1007/s10709-010-9519-z PMID: 19882364 Retracted.
-
Loss of the bloom syndrome helicase increases DNA ligase 4-independent genome rearrangements and tumorigenesis in aging Drosophila.Genome Biol. 2011 Dec 19;12(12):R121. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-12-r121. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 22183041 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila brca2 is required for mitotic and meiotic DNA repair and efficient activation of the meiotic recombination checkpoint.PLoS Genet. 2008 Feb;4(2):e31. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040031. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18266476 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

