eIF4E is a central node of an RNA regulon that governs cellular proliferation
- PMID: 17074885
- PMCID: PMC2064519
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200607020
eIF4E is a central node of an RNA regulon that governs cellular proliferation
Abstract
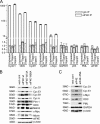
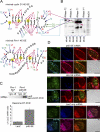
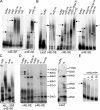
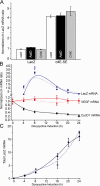
This study demonstrates that the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E is a critical node in an RNA regulon that impacts nearly every stage of cell cycle progression. Specifically, eIF4E coordinately promotes the messenger RNA (mRNA) export of several genes involved in the cell cycle. A common feature of these mRNAs is a structurally conserved, approximately 50-nucleotide element in the 3' untranslated region denoted as an eIF4E sensitivity element. This element is sufficient for localization of capped mRNAs to eIF4E nuclear bodies, formation of eIF4E-specific ribonucleoproteins in the nucleus, and eIF4E-dependent mRNA export. The roles of eIF4E in translation and mRNA export are distinct, as they rely on different mRNA elements. Furthermore, eIF4E-dependent mRNA export is independent of ongoing RNA or protein synthesis. Unlike the NXF1-mediated export of bulk mRNAs, eIF4E-dependent mRNA export is CRM1 dependent. Finally, the growth-suppressive promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) inhibits this RNA regulon. These data provide novel perspectives into the proliferative and oncogenic properties of eIF4E.
Figures

Similar articles
-
eIF4E promotes nuclear export of cyclin D1 mRNAs via an element in the 3'UTR.J Cell Biol. 2005 Apr 25;169(2):245-56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200501019. Epub 2005 Apr 18. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15837800 Free PMC article.
-
Human inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression depends on chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1)- and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (elF4E)-mediated nucleocytoplasmic mRNA transport.Nitric Oxide. 2013 Apr 1;30:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.02.083. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Nitric Oxide. 2013. PMID: 23471078
-
PML RING suppresses oncogenic transformation by reducing the affinity of eIF4E for mRNA.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 15;20(16):4547-59. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4547. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11500381 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA export and cancer.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Jan-Feb;3(1):13-25. doi: 10.1002/wrna.101. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 21796793 Review.
-
The emerging roles of translation factor eIF4E in the nucleus.Differentiation. 2002 Mar;70(1):10-22. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.2002.700102.x. Differentiation. 2002. PMID: 11963652 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-molecule induction of phospho-eIF4E sumoylation and degradation via targeting its phosphorylated serine 209 residue.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 20;6(17):15111-21. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3615. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25915158 Free PMC article.
-
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E reprograms alternative splicing.EMBO J. 2023 Apr 3;42(7):e110496. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021110496. Epub 2023 Feb 27. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 36843541 Free PMC article.
-
Viral subversion of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking.Traffic. 2014 Feb;15(2):127-40. doi: 10.1111/tra.12137. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 24289861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-induced Eukaryotic Translational Regulatory Mechanisms.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 2:arXiv:2405.01664v1. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: J Clin Med Sci. 2024;8(2):1000277. PMID: 38745702 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Identification of a novel RNA giant nuclear body in cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4724-34. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6619. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26678034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachmann, M., and T. Moroy. 2005. The serine/threonine kinase Pim-1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37:726–730. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y.C., Y.N. Su, P.C. Chou, W.C. Chiang, M.C. Chang, L.S. Wang, S.C. Teng, and K.J. Wu. 2005. Overexpression of NBS1 contributes to transformation through the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 280:32505–32511. - PubMed
-
- Clemens, M.J., and U.A. Bommer. 1999. Translational control: the cancer connection. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

