Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and transforming growth factor-beta1/Smad signaling pathways modulates the development of fibrosis in adriamycin-induced nephropathy
- PMID: 17071578
- PMCID: PMC1780196
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060169
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and transforming growth factor-beta1/Smad signaling pathways modulates the development of fibrosis in adriamycin-induced nephropathy
Abstract
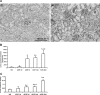
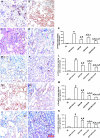
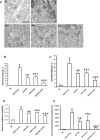
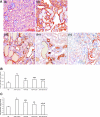
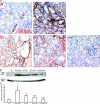
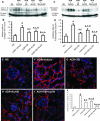
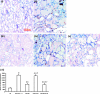
Inflammation and fibrogenesis are the two determinants of the progression of renal fibrosis, the common pathway leading to end-stage renal disease. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1/Smad signaling pathways play critical roles in inflammation and fibrogenesis, respectively. The present study examined the beneficial renoprotective effect of combination therapy using the p38 MAPK pathway inhibitor (SB203580) and a TGF-beta receptor I (ALK5) inhibitor (ALK5I) in a mouse model of adriamycin (ADR) nephrosis. The p38 MAPK and TGF-beta1/Smad2 signaling pathways were activated in ADR-induced nephropathy in a sequential time course manner. Two weeks after ADR injection, the combined administration of SB203580 (1 mg/kg/24 hours) and ALK5I (1 mg/kg/24 hours) markedly reduced p38 MAPK and Smad2 activities. Moreover, the co-administration of SB203580 and ALK5I to ADR-injected mice resulted in a down-regulation of total and active TGF-beta1 production, reduced myofibroblast accumulation, and decreased expression of collagen type IV and fibronectin. In these mice, retardation in the development of glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis was observed. In conclusion, although p38 MAPK and TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathways are distinct they coordinate the progression of renal fibrosis in ADR nephrosis. The co-administration of a p38 MAPK inhibitor and an ALK5 inhibitor may have potential applications in the treatment of renal fibrosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathways rescues bone marrow-derived peritubular capillary endothelial cells in adriamycin-induced nephrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006 Oct;17(10):2799-811. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006020130. Epub 2006 Sep 7. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16959826
-
Inhibition of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced extracellular matrix with a novel inhibitor of the TGF-beta type I receptor kinase activity: SB-431542.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;62(1):58-64. doi: 10.1124/mol.62.1.58. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12065755
-
Gefitinib attenuates transforming growth factor-β1-activated mitogen-activated protein kinases and mitogenesis in NRK-49F cells.Transl Res. 2011 Oct;158(4):214-24. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21925118
-
Mechanism of transforming growth factor-beta1 signaling:Kidney Int Suppl. 2000 Sep;77:S53-8. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000. PMID: 10997691 Review.
-
ALK5 inhibition in renal disease.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;3(2):204-8. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4892(03)00002-x. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12681245 Review.
Cited by
-
Smad3 promotes adverse cardiovascular remodeling and dysfunction in doxorubicin-treated hearts.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Dec 1;323(6):H1091-H1107. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00312.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36269647 Free PMC article.
-
Novel therapies for FSGS: preclinical and clinical studies.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015 Mar;22(2):e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2014.10.001. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25704355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chlorogenic Acid (CGA) Isomers Alleviate Interleukin 8 (IL-8) Production in Caco-2 Cells by Decreasing Phosphorylation of p38 and Increasing Cell Integrity.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 4;19(12):3873. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123873. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30518116 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Blockade of Smad3 and JNK Pathways Ameliorates Progressive Fibrosis in Folic Acid Nephropathy.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 9;10:880. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00880. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31447676 Free PMC article.
-
Salinomycin and other polyether ionophores are a new class of antiscarring agent.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3563-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601872. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25538236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ono K, Han J. The p38 signal transduction pathway activation and function. Cell Signal. 2000;12:1–13. - PubMed
-
- New L, Han J. The p38 MAP kinase pathway and its biological function. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1998;8:220–228. - PubMed
-
- Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, Takagi M, Matsumoto K, Miyazono K, Gotoh Y. Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science. 1997;275:90–94. - PubMed
-
- Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers JS, Dickens M, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Davis RJ. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7420–7426. - PubMed
-
- Yoshinari D, Takeyoshi I, Koibuchi Y, Matsumoto K, Kawashima Y, Koyama T, Ohwada S, Morishita Y. Related articles, effects of a dual inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 on lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats: involvement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:628–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

