Functional characterization of the promoter for the mouse SPTLC2 gene, which encodes subunit 2 of serine palmitoyltransferase
- PMID: 17070807
- PMCID: PMC1698862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.10.025
Functional characterization of the promoter for the mouse SPTLC2 gene, which encodes subunit 2 of serine palmitoyltransferase
Abstract
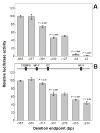
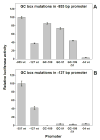
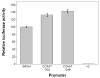
A series of luciferase reporter constructs was prepared from a 1035-bp fragment of mouse genomic DNA flanking the 5'-coding sequence for the SPTLC2 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase, the initial enzyme of de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis. The full-length DNA fragment promoted strong reporter gene expression in NIH3T3 cells while deletion and site-directed mutagenesis indicated that the proximal 335 bp contain initiator and downstream promoter elements, two proximal GC boxes that appear to stimulate transcription in a cooperative manner, and several additional elements whose activity cannot be accounted for by known factor binding sites. These findings provide insight into the control mechanisms for transcription of mammalian SPTLC2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endotoxin activates de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis via nuclear factor kappa B-mediated upregulation of Sptlc2.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011 Feb;94(1-2):44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2010.12.003. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011. PMID: 21167294 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of the human and murine polo-like kinase (Plk) promoter.Oncogene. 1995 Nov 2;11(9):1793-800. Oncogene. 1995. PMID: 7478607
-
Promoter cloning and characterization of the rabbit BK channel beta1 subunit gene.Gene. 2009 Jun 1;438(1-2):33-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.03.001. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19303925
-
Transcriptional regulation of the mouse PNRC2 promoter by the nuclear factor Y (NFY) and E2F1.Gene. 2005 Nov 21;361:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.07.012. Epub 2005 Sep 21. Gene. 2005. PMID: 16181749
-
Serine Palmitoyltransferase Subunit 3 and Metabolic Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1372:47-56. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-0394-6_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35503173 Review.
Cited by
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor activates ceramide biosynthesis in mice contributing to hepatic lipogenesis.Toxicology. 2021 Jun 30;458:152831. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152831. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 34097992 Free PMC article.
-
The cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) regulates the expression of acid ceramidase (ASAH1) in H295R human adrenocortical cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Aug;1791(8):706-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.03.005. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19298866 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin activates de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis via nuclear factor kappa B-mediated upregulation of Sptlc2.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011 Feb;94(1-2):44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2010.12.003. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011. PMID: 21167294 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte specific deficiency of serine palmitoyltransferase subunit 2 reduces ceramide but leads to cardiac dysfunction.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 25;287(22):18429-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.296947. Epub 2012 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22493506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanada K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1632:16–30. - PubMed
-
- Wei J, Tokumbo Y, Liepelt M, Momin A, Wang E, Hanada K, Merrill AH. In: Serine Palmitoyltransferase in Sphingolipid Biology. Hirabayashi Y, Igarashi Y, Merrill AH, editors. Springer; Tokyo: 2006. pp. 25–47.
-
- Hanada K, Nishijima M, Akamatsu Y. A temperature-sensitive mammalian cell mutant with thermolabile serine palmitoyltransferase for the sphingolipid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:22137–22142. - PubMed
-
- Chigorno V, Giannotta C, Ottico E, Sciannamblo M, Mikulak J, Prinetti A, Sonnino S. Sphingolipid uptake by cultured cells: complex aggregates of cell sphingolipids with serum proteins and lipoproteins are rapidly catabolized. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:2668–2675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

