Sog/Chordin is required for ventral-to-dorsal Dpp/BMP transport and head formation in a short germ insect
- PMID: 17050690
- PMCID: PMC1637578
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605154103
Sog/Chordin is required for ventral-to-dorsal Dpp/BMP transport and head formation in a short germ insect
Abstract
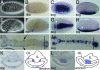
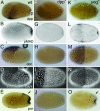
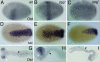
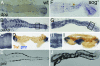
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling plays a major role in dorsoventral patterning in vertebrates and in Drosophila. Remarkably, in Tribolium, a beetle with an ancestral type of insect development, early BMP/dpp exhibits differential expression along the anteroposterior axis. However, the BMP/Dpp inhibitor Sog/chordin is expressed ventrally and establishes a dorsal domain of BMP/Dpp activity by transporting BMPs toward the dorsal side, like in Drosophila. Loss of Tribolium Sog not only abolishes dorsoventral polarity in the ectoderm, but also leads to the complete absence of the CNS. This phenotype suggests that sog is the main BMP antagonist in Tribolium, in contrast to vertebrates and Drosophila, which possess redundant antagonists. Surprisingly, Sog also is required for head formation in Tribolium, as are the BMP antagonists in vertebrates. Thus, in Tribolium, the system of BMP and its antagonists is less complex than in Drosophila or vertebrates and combines features from both, suggesting that it might represent an ancestral state.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolution of extracellular Dpp modulators in insects: The roles of tolloid and twisted-gastrulation in dorsoventral patterning of the Tribolium embryo.Dev Biol. 2010 Sep 1;345(1):80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.05.019. Epub 2010 May 26. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20510683
-
A conserved system for dorsal-ventral patterning in insects and vertebrates involving sog and chordin.Nature. 1995 Jul 20;376(6537):249-53. doi: 10.1038/376249a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7617035
-
A positive role for Short gastrulation in modulating BMP signaling during dorsoventral patterning in the Drosophila embryo.Development. 2001 Oct;128(19):3831-41. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.19.3831. Development. 2001. PMID: 11585808
-
Conservation of dorsal-ventral patterning in arthropods and chordates.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Aug;6(4):424-31. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80063-3. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. PMID: 8791529 Review.
-
Holy Tolloido: Tolloid cleaves SOG/Chordin to free DPP/BMPs.Trends Genet. 1998 Apr;14(4):127-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(98)01431-0. Trends Genet. 1998. PMID: 9594656 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Striking parallels between dorsoventral patterning in Drosophila and Gryllus reveal a complex evolutionary history behind a model gene regulatory network.Elife. 2021 Mar 30;10:e68287. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68287. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33783353 Free PMC article.
-
The mlpt/Ubr3/Svb module comprises an ancient developmental switch for embryonic patterning.Elife. 2019 Mar 21;8:e39748. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39748. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30896406 Free PMC article.
-
Highly conserved and extremely evolvable: BMP signalling in secondary axis patterning of Cnidaria and Bilateria.Dev Genes Evol. 2024 Jun;234(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00427-024-00714-4. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Dev Genes Evol. 2024. PMID: 38472535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity and robustness of bone morphogenetic protein pattern formation.Development. 2021 Apr 6;148(7):dev192344. doi: 10.1242/dev.192344. Print 2021 Apr 1. Development. 2021. PMID: 33795238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of SMAD1/5 target genes in a sea anemone reveals ZSWIM4-6 as a novel BMP signaling modulator.Elife. 2024 Feb 7;13:e80803. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80803. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38323609 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

