Modulation of host gene expression by the K15 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
- PMID: 17050609
- PMCID: PMC1797256
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00648-06
Modulation of host gene expression by the K15 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
Abstract
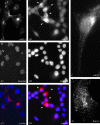
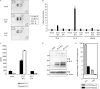
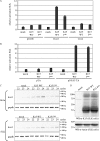
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) contains several open reading frames (ORFs) encoding proteins capable of initiating signal transduction pathways. Among them is the K15 ORF, which consists of eight exons encoding a protein with 12 predicted transmembrane domains and a cytoplasmic C terminus. When transiently expressed, the 8-exon K15 transcript gives rise to a protein with an apparent molecular mass of 45 kDa. K15 interacts with cellular proteins, TRAF (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor) and Src kinases, and activates AP-1, NF-kappaB, and the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) c-jun-N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. This signaling activity of K15 is related to phosphorylation of Y(481) of the K15 SH2-B motif Y(481)EEV. In this study we demonstrate the expression of an endogenous 45-kDa K15 protein in KSHV BAC36-infected epithelial cells. This endogenous K15 protein shows the same intracellular localization as transiently expressed K15, and expression kinetic studies suggest it to be a lytic gene. We have further determined the downstream target genes of K15 signaling using DNA oligonucleotide microarrays. We demonstrate that K15 is capable of inducing expression of multiple cytokines and chemokines, including interleukin-8 (IL-8), IL-6, CCL20, CCL2, CXCL3, and IL-1alpha/beta, as well as expression of Dscr1 and Cox-2. In epithelial cells, K15-induced upregulation of most genes was dependent on phosphorylation of Y(481), whereas in endothelial cells mutation of Y(481) did not result in a complete loss of Dscr1 and Cox-2 expression and NFAT-activity. Our study establishes K15 as one of the KSHV lytic genes that are inducing expression of multiple cytokines, which have been shown to play an important role in KSHV-associated pathogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multi-transmembrane protein K15 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus targets Lyn kinase in the membrane raft and induces NFAT/AP1 activities.Exp Mol Med. 2008 Oct 31;40(5):565-73. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.5.565. Exp Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18985015 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB pathways by a Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K15 membrane protein.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9346-58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9346-9358.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915550 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus K15 protein contributes to virus-induced angiogenesis by recruiting PLCγ1 and activating NFAT1-dependent RCAN1 expression.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002927. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002927. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23028325 Free PMC article.
-
The M type K15 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus regulates microRNA expression via its SH2-binding motif to induce cell migration and invasion.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(2):622-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00869-08. Epub 2008 Oct 29. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18971265 Free PMC article.
-
The essential role of calcium in induction of the DSCR1 (ADAPT78) gene.Biofactors. 2001;15(2-4):91-3. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520150208. Biofactors. 2001. PMID: 12016333 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
K1 and K15 of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Are Partial Functional Homologues of Latent Membrane Protein 2A of Epstein-Barr Virus.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7248-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00839-15. Epub 2015 May 6. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25948739 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus lytic transactivator Zta enhances chemotactic activity through induction of interleukin-8 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.J Virol. 2008 Apr;82(7):3679-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02301-07. Epub 2008 Jan 30. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18234802 Free PMC article.
-
Viral control of mitochondrial apoptosis.PLoS Pathog. 2008 May 30;4(5):e1000018. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000018. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18516228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Sequencing Reveals that Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection Mimics Hypoxia Gene Expression Signature.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 3;13(1):e1006143. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006143. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28046107 Free PMC article.
-
Array-based transcript profiling and limiting-dilution reverse transcription-PCR analysis identify additional latent genes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(11):5565-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02723-09. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20219929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, M., and Y. Sato. 2001. cDNA microarray analysis of the gene expression profile of VEGF-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 4:289-298. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, Y., E. S. Jaffe, Y. Chang, K. Jones, J. Teruya-Feldstein, P. S. Moore, and G. Tosato. 1999. Angiogenesis and hematopoiesis induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6. Blood 93:4034-4043. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, Y., and G. Tosato. 1999. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in the pathogenesis of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-infected primary effusion lymphomas. Blood 94:4247-4254. - PubMed
-
- Asou, H., J. W. Said, R. Yang, R. Munker, D. J. Park, N. Kamada, and H. P. Koeffler. 1998. Mechanisms of growth control of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus-associated primary effusion lymphoma cells. Blood 91:2475-2481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

